Food Supplements Regulations Guide Sample

Introduction
The content that follows is a sample preview of a Food Supplements Regulation Guide in SGS DIGICOMPLY. All food Supplements Guides can be accessed from within the SGS DIGICOMPLY platform. Here you will find sample content that is cut for preview purposes only.
The text that you find here has been edited for preview only and shall not be used as reference. Images and tables have been resized for this preview and have been made not readable on purpose.
Table of Contents
SUMMARY
The scope of this document is to provide a general legislation framework assessment in the European Union for food supplements. This work aims to conduct a regulatory analysis that covers all requirements on composition, labelling, advertising, and registration. It gives an introduction for selling food supplements on a certain market to introduce into local administrative procedures and to create the label. This report provides an overview and should not be taken as legal advice.
GLOBAL OVERVIEW
The legal situation of Food supplements worldwide is really complex.
European Union Overview
The European Union is one of the supplements' main markets. Food supplements are classified as foodstuff and are regulated by the EU Directive 2002/46.
Definition
"Food supplements" are defined in EU DIRECTIVE
...“‘food supplements’ means foodstuffs the purpose of which is to supplement the normal diet.
INGREDIENTS
A wide range of nutrients and other ingredients might be present in food supplements, including, but not limited to, vitamins, minerals, amino acids, essential fatty acids, fiber, and various plants and herbal extracts.
1. Novel food
Ingredients in food supplements must not be considered novel:
Novel food means any food that was not used for human consumption to a significant degree within the Union before 15 May 1997.
2. Therapeutic purpose
In addition to Novel food purposes, ingredients in food supplements cannot exert a pharmacological, immunological, or metabolic action.
3. ACTIVE INGREDIENTS
Except for specificities mentioned in the "general principles" part above, very few regulatory requirements for active ingredients are harmonized at the EU/Communautary level.
1. Vitamins and Minerals
In the EU, the regulations for vitamins and minerals are a bit more harmonized than other active ingredients for food supplements.
2. Botanicals
From a regulatory point of view and as for the substances, botanicals authorized in food supplements are not harmonized at the EU level.
3. Microorganisms
Microorganisms can be authorized in food supplements as ingredients with the nutritional or physiological effect but as currently there is no positive list of authorized species or strains in European regulations.
4. NON-ACTIVE INGREDIENTS
-
-
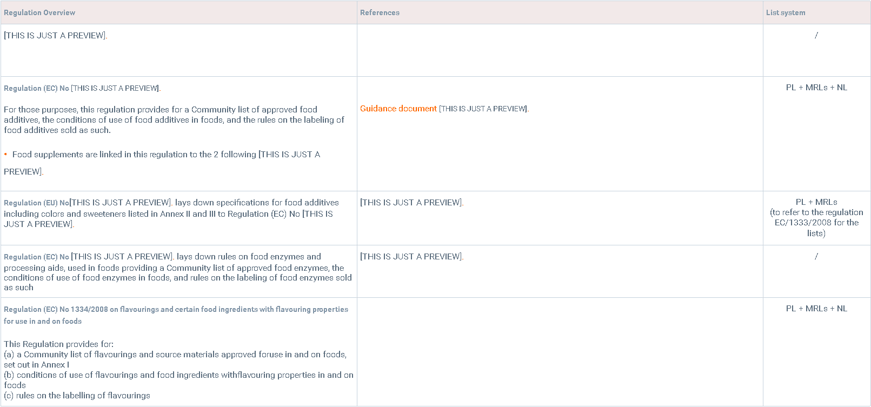
Food additives and flavoring
The below table summarizes the main regulations for food additives, food enzymes and flavorings:
-
-
-
Restricted ingredients
The table below summarizes ingredients that are restricted by the EU regulations but cannot be considered as an exhaustive list.
-
-
-
Prohibited ingredients
The principle of basis is that food consumption must be safe for the consumer.
-
LABELLING
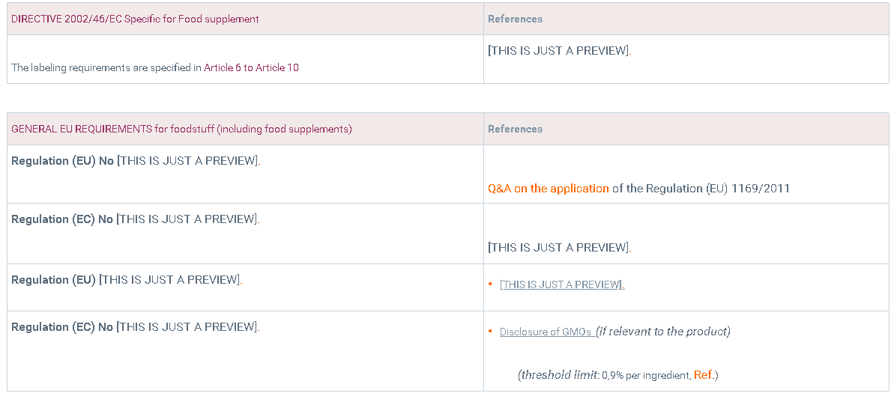
SGS DIGICOMPLY provides an overview of all relevant regulations relevant for labelling. Here is just a sample
1. Relevant regulations
2. Mandatory mentionings
EU labeling legislation for food supplements is specified in Directive 2002/46/EC and must be aligned with general labeling requirements.
3. Voluntary mentions
CLAIMS
According to Regulation 1924/2006 on nutrition and health claims made on foods the different definitions of claims are as follows:
Claim: means any message or representation, which is not mandatory under Community or national legislation, including pictorial, graphic or symbolic representation, in any form, which states, suggests, or implies that a food has particular characteristics.
Nutrition claim: means any claim that states, suggests, or implies that a food has particular beneficial nutritional properties due to:
-the energy (calorific value) it provides; provides at a reduced or increased rate; or does not provide
Health claim: means any claim that states, suggests, or implies that a relationship exists between a food category, a food, or one of its constituents and health.


The so-called minimum limit for vitamins and minerals to be on the label of the product.
Organic regulations, if applicable:
PRODUCT NOTIFICATION
Member States may, for monitoring purposes, request notification of the placing on the market in their territory of a food supplement.
The national rules/regulations must be taken into account at this stage as the marketing procedure of food supplements in the national territory is not harmonized at the EU level.
