Supply chain risk management in the food industry is crucial for maintaining food safety, quality, and compliance. The complexity of global food supply chains presents numerous challenges, including diverse sourcing, varying regulations, and potential disruptions. Effective risk management helps mitigate these challenges by identifying, assessing, and controlling risks throughout the supply chain.
In this article, we'll explore the key aspects of supply chain risk management, including what it entails, the major risks in the food industry supply chain, and strategies for effective risk management. We'll also highlight how SGS Digicomply can be your partner in navigating these complexities.
What is Supply Chain Risk Management?
It is the structured process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that may disrupt the supply chain, affect product quality, or compromise food safety in the food industry. These activities are carried out to make sure that food products are safe, comply with regulatory standards, and reach consumers without a hitch.
Effective supply chain risk management involves:
- Risk Identification: Recognizing potential threats such as contamination, supply disruptions, and regulatory changes.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the likelihood and impact of identified risks.
- Risk Mitigation: Implementing strategies to prevent or reduce the impact of risks, including supplier audits, quality control measures, and emergency response plans.
This process is essential for maintaining compliance with food safety regulations and industry standards, ultimately supporting the overall stability and success of food supply chains.
Major Risks in the Food Industry Supply Chain
The food industry supply chain faces a variety of significant risks that can affect safety, quality, and continuity. Understanding these risks is essential for effective supply chain risk management. The major risks include:
- Biological Hazards: Contamination from bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens that can cause foodborne illnesses.
- Chemical Contaminants: Presence of harmful chemicals, such as pesticides, heavy metals, and food additives.
- Physical Hazards: Foreign objects like glass, metal, or plastic that can cause injury.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Natural disasters, geopolitical events, and transportation issues that can interrupt the supply chain.
- Regulatory Changes: Variations in food safety regulations across different countries that can complicate compliance efforts.
Each of these risks requires specific strategies to identify, assess, and mitigate them effectively. By addressing these risks proactively, food businesses can protect their supply chains and ensure the safety and quality of their products.
Identifying and Assessing Risks
Identifying and assessing risks in the food industry supply chain is a critical step toward ensuring food safety and compliance. This section will cover various techniques and methods used to recognize and evaluate potential risks.
Risk Identification Techniques
-
Supplier Audits and Inspections
- Regular audits and inspections help identify potential risks at the supplier level.
- Ensures that suppliers adhere to safety and quality standards.
-
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points)
- A systematic approach to identifying biological, chemical, and physical hazards.
- Involves analyzing processes from production to distribution to pinpoint critical control points.
-
Regulatory and Market Intelligence
- Monitoring changes in regulations and market trends to foresee potential risks.
- Helps in staying compliant with the latest standards and avoiding disruptions.
-
Historical Data Analysis
- Using past data to identify patterns and trends that could indicate future risks.
- Enables proactive measures based on historical incidents and outcomes.
-
Stakeholder Feedback
- Gathering insights from suppliers, customers, and other stakeholders.
- Helps in identifying risks that may not be apparent through internal audits alone.
Risk Assessment Methods
-
Qualitative Risk Assessment
- Subjective evaluation based on expert judgment and stakeholder input.
- Involves categorizing risks by severity and likelihood.
-
Quantitative Risk Assessment
- Uses numerical data to measure and analyze risks.
- Techniques include statistical analysis and probability assessments.
-
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- Identifies potential failure points and their impact on the supply chain.
- Prioritizes risks based on their severity, occurrence, and detectability.
-
Scenario Analysis
- Evaluates potential outcomes of different risk scenarios.
- Helps in planning responses to various possible disruptions.
-
Risk Matrix
- A visual tool that maps out risks based on their likelihood and impact.
- Facilitates easy comparison and prioritization of risks.
Importance of Data and Analytics
-
Real-Time Monitoring
- Continuous data collection and monitoring of supply chain activities.
- Enables immediate detection and response to emerging risks.
-
Predictive Analytics
- Uses advanced algorithms to predict potential risks before they occur.
- Helps in taking preemptive actions to mitigate risks.
-
Big Data Integration
- Combining data from multiple sources for comprehensive risk analysis.
- Enhances the accuracy and reliability of risk assessments.
This proactive approach ensures that potential issues are addressed before they escalate, maintaining the safety, quality, and integrity of food products.
Strategies for Effective Supply Chain Risk Management
Effective supply chain risk management in the food industry involves implementing a combination of preventive measures, proactive strategies, and technological solutions. Here are some key strategies:
Preventive Measures and Controls
-
Supplier Management and Audits
- Conduct regular audits and assessments of suppliers to ensure they meet quality and safety standards.
- Establish strong relationships and clear communication channels with suppliers to quickly address any issues.
-
Quality Control Measures
- Implement rigorous quality control processes at each stage of the supply chain.
- Use standardized procedures for testing and verifying the safety and quality of food products.
-
Traceability Systems
- Develop robust traceability systems to track food products from farm to fork.
- Use barcodes, RFID tags, and blockchain technology to enhance transparency and accountability.
-
Crisis Management and Response Plans
- Create detailed crisis management plans to address potential supply chain disruptions.
- Conduct regular drills and training to ensure all stakeholders are prepared for emergencies.
Proactive Strategies
-
Risk Mitigation Strategies
- Diversify suppliers and sourcing locations to reduce dependency on a single source.
- Implement inventory management practices to buffer against supply chain disruptions.
-
Collaborative Risk Management
- Foster collaboration among supply chain partners to share information and resources.
- Engage in joint risk assessments and mitigation planning with suppliers and other stakeholders.
-
Regulatory Compliance
- Stay informed about changing regulations and ensure compliance with all relevant food safety standards.
- Work with regulatory experts to navigate complex international requirements.
-
Continuous Improvement
- Regularly review and update risk management practices based on new data and industry developments.
- Use feedback from audits, inspections, and incident reports to improve processes and controls.
Technological Solutions
-
AI and Machine Learning
- Utilize AI and machine learning algorithms to analyze data and predict potential risks.
- Implement automated systems for monitoring and managing supply chain activities.
-
Blockchain Technology
- Adopt blockchain technology to enhance transparency and traceability in the supply chain.
- Use blockchain to verify the authenticity and origin of food products.
-
Predictive Analytics
- Employ predictive analytics to forecast potential disruptions and take preemptive actions.
- Use data-driven insights to make informed decisions about risk management.
These measures also help in building a resilient supply chain capable of withstanding various challenges and disruptions.
SGS Digicomply: Your Partner in Supply Chain Risk Management
SGS Digicomply stands out as a robust supply chain risk management software, offering a suite of tools designed to streamline and enhance food safety and regulatory compliance. Leveraging advanced AI and big data analytics, SGS Digicomply transforms complex data into actionable insights, helping businesses manage risks more effectively.
Food Safety Intelligence Hub
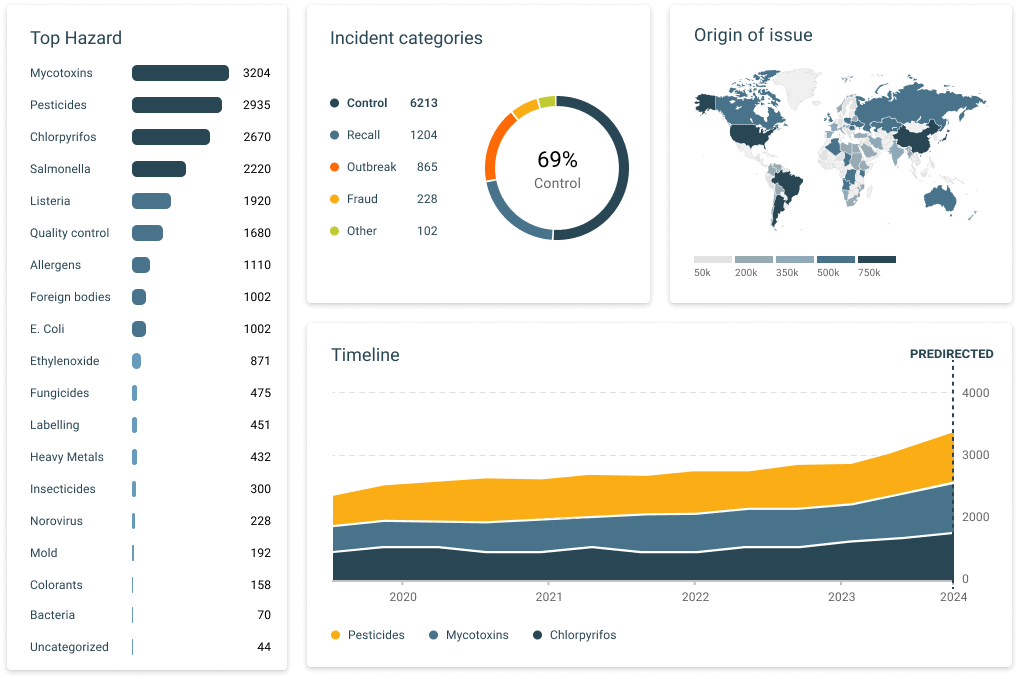
The Food Safety Intelligence Hub aggregates and analyzes data from thousands of sources, providing real-time insights into emerging risks. By utilizing AI, it filters and contextualizes vast amounts of information, enabling proactive risk management and timely decision-making. Explore these demos to see this tool in action.
Regulatory Intelligence Hub
Navigating the regulatory landscape can be daunting, but the Regulatory Intelligence Hub simplifies this process. Covering standards and requirements from over 150 jurisdictions, it ensures that businesses remain compliant globally. AI-powered data retrieval makes it easier to stay updated with ever-changing regulations, reducing the risk of non-compliance. Explore these demos to see this tool in action.

Global Ingredient Monitor
Monitoring ingredients across the supply chain is crucial for maintaining safety and quality. The Global Ingredient Monitor offers comprehensive tracking and analysis of ingredients, identifying potential risks before they become critical issues. This feature supports transparency and traceability, essential components of a robust risk management strategy. Explore these demos to see this tool in action.

Horizon Scanning
Horizon Scanning is an invaluable tool for anticipating future risks and trends. By continuously scanning the regulatory and market environment, it helps businesses stay ahead of potential threats. AI-driven insights from Horizon Scanning allow companies to adapt and respond proactively, maintaining resilience in their supply chains. Explore these demos to see this tool in action.
.png?width=1246&height=924&name=Flexible%20Notifications%20and%20Customizable%20Dashboard%20(1).png)
AI and Big Data Analytics
The core of the SGS Digicomply platform's capabilities relates to the use of AI and Big Data Analytics, through which it can quickly and accurately process and analyze humongous datasets. The result is a powerful system that not only identifies varied risks but also provides deep insights into how they are likely to impact business processes, hence empowering an entity to make informed and strategic decisions.
SGS Digicomply integrates all of these very sophisticated functionalities into one platform, providing an answer to supply chain risk management in the food industry. SGS Digicomply provides real-time data, predictive analytics, and holistic monitoring to enable businesses to effectively navigate through the complexities of food safety and regulatory compliance, giving them the ability to efficiently and confidently deliver safe, high-quality products to the market. Explore SGS Digicomply platform.





.webp?width=1644&height=1254&name=Food%20Safety%20Dashboard%201%20(1).webp)
