Food safety is even more critical now than ever in this fast-moving food industry. Supply chains have become complex, and thus, the exposure to contamination and foodborne illnesses has increased. Therefore, having sound risk assessment strategies is more important than ever. Traditional methods served pretty well, and now advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence step in to take food safety to a new level. The following guide considers how AI is changing the face of food safety risk assessments and how industry leaders can leverage such innovations for improved risk management.
What is Food Safety Risk Assessment?
Food safety risk assessment is the structured process of identifying, assessing, and controlling the risks posed by food safety hazards. This process involves hazard identification, evaluation of the severity and likelihood of adverse consequences, and control measures to reduce such risks. It ensures that food products offered for consumption are safe and meet specified regulatory standards. The bottom line is the protection of public health from foodborne illnesses and the assurance of the integrity of the food supply chain.
Food Safety Risk Assessment Examples
Food safety risk assessment is important to identify and put control over the hazards across food production. Some elaborated examples include the following:
- Salmonella in Poultry: One of the common examples, wherein the risk assessment looks at where contamination has originated, feeding, water conditions, and handling practices. The mitigative measures will thus be strict hygiene practices, regular monitoring, and vaccination programs.
- Listeria in Ready-to-Eat Foods: In this case, the risk assessments are made against Listeria contamination during processing and storage. The control measures set out under this scenario include temperature control, surface sanitation, and regular microbial testing.
- Allergens in Processed Foods: It involves assessing the risk due to cross-contamination by ingredients likely to cause allergies. Some of the control measures applied are segregation of the allergenic ingredients, clear labeling, and cleaning programs.
- Chemical Contaminants in Produce: Controls on pesticide residues and heavy metals in fruits and vegetables are based on rigid testing, sourcing from trusted suppliers, and adherence to guidelines for the safe usage of pesticides.
Key Elements of Food Safety Risk Assessment
A good food safety risk assessment has a number of essential elements, all of which are central to the production of a safe and quality food product.
- Hazard identification: This is essentially the first step in the process. This would include hazards that are biological, chemical, and physical in nature. Examples of hazards are the following: biological—bacteria, viruses; chemical—pesticides, food additives; physical—foreign objects like glass or metal. Thorough hazard identification will ensure that all possible risks are considered.
- Risk Analysis: The likelihood and severity of the identified hazards are assessed. The quantitative or qualitative analysis ranks the risk, providing resistance to those that could most affect food safety.
- Control Measures: Develop and implement control measures that will reduce identified risks. These include sanitation schedules, cooking instructions, and raw material supply specifications. Effective control measures are those which are hazard-specific and operation-specific.
- Monitoring and Verification: This process provides continuous assurance that the implemented control measures are appropriate and are properly maintained. Verification through regular checks proves compliance and shows areas for improvement.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: Proper documentary records on the risk assessment, control measure, and monitoring are kept in detail for their traceability and compliance with regulations. Good documentation sustains transparency and accountability.
How AI Can Enhance Food Safety Risk Assessment Processes
Artificial intelligence is currently changing many industries, and food safety makes no exception. It would be possible for businesses to have more efficient and accurate food safety risk assessments if AI were used. Here's how AI enhances these processes:
- Data Collection and Analysis: AI systems can process large amounts of data from various sources, such as regulatory databases, scientific research articles, and social media platforms. This can be used in finding patterns or trends that could show possible hazardous situations, hence posing a danger to human beings, which would otherwise have been difficult and tiresome to project.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can make use of past data to project future risks and provide for proactive, not reactive, measures. For instance, impending regulatory changes or new food safety threats could be predicted using machine learning models that read and analyze data from government alerts, scientific publications, and industry reports.
- Routine Task Automation: AI is empowered to automate routine tasks in scanning, updating, and maintaining compliance regarding food safety across multiple jurisdictions. This not only reduces the chances of human error but also frees up resources so that time becomes available to deal with more strategic aspects associated with risk management.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts: AI can monitor food production environments in real-time. It can instantaneously detect any deviation from the set safety standards and alert for action to be taken to correct such. This real-time capability is critical to preventing contamination at an early stage, before it spreads.
- Improved traceability: Artificial intelligence within supply chains improves traceability of food products by way of integrating data from all stages of a product's production and distribution. This kind of complete line-of-sight visibility empowers companies to locate sources of contamination at a very rapid rate and to conduct swifter recalls when such a need actually does arise.
- Better Decision-Making: AI offers actionable insights through advanced analytics, which support more informed decision-making. Using AI-generated reports, risk managers could gauge the intensity and possibility of risks and act on them accordingly.
In this direction, AI applied to food safety risk assessment methodologies will help industry leaders achieve higher accuracy, efficiency, and reliability in their safety protocols. In addition to preventing foodborne illness, this technological advancement assures compliance with regulatory standards that ensure the safeguarding of public health.
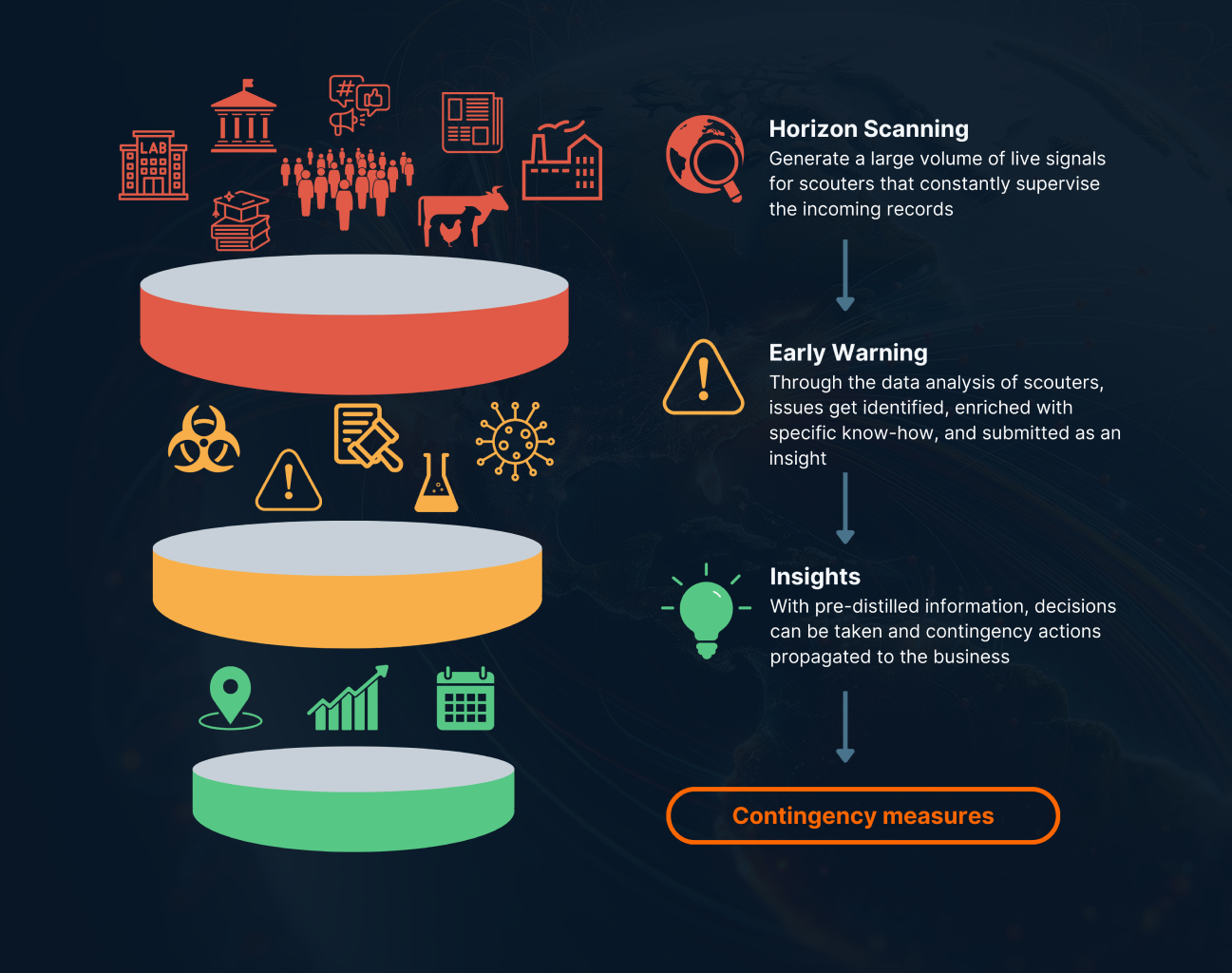
Horizon Scanning and Its Role in Food Safety Risk Management
To further enhance our understanding of food safety risk assessment, it is essential to consider the horizon scanning universe.
.png?width=1093&height=445&name=Horizon%20Scanning%20(3).png)
This concept involves three critical stages that help in identifying and managing risks effectively:
- Early Warning (Short Term): Rapid alert systems that require immediate action. This stage focuses on identifying immediate threats that need quick response to prevent further escalation.
- Emerging Risk Identification (Medium Term): Screening systems that increase preparedness and initiate risk assessment. This stage helps in recognizing new and evolving risks that could impact food safety in the near future.
- Foresight (Long Term): Driver and scenario analysis that affects strategic actions. This stage involves analyzing long-term trends and potential future scenarios to inform strategic planning and decision-making.
These stages are integral to a comprehensive food safety risk assessment strategy, ensuring that organizations are well-prepared to identify, assess, and mitigate risks at different time horizons.
How to Do Food Safety Risk Assessment
Food safety risk assessment consists of some very crucial steps that facilitate the identification, evaluation, and mitigation of potential hazards along the food chain. On protecting public health and regulatory compliance, each step calls for careful planning and execution. The following is an in-depth guide on how to conduct a food safety risk assessment.
Step 0: Preparing for your Risk Assessment
Preparation is the general first step in any formative and effective risk assessment. It involves the acquirement of required resources, formulation of a qualified team, and setting the limits and objectives of assessment.
Key Actions:
- Establish a Multidisciplinary Team: The experts should include food safety, microbiology, chemistry, and relevant production processes. Diverse expertise ensures that all possible hazards are understood.
- Define the scope and goals of the risk assessment: Clearly define what it will cover, including products, processes, and hazards for assessment.
- Collect background information that sets the context, which is essential to determine what could represent a pertinent risk.
- Develop a detailed risk assessment plan in terms of steps, methods, and timing, in such a way that all participants are in agreement.
Step 1: Hazard Identification
Identifying potential hazards is the first formal step in the risk assessment process. This involves a thorough examination of the entire food production process to pinpoint where and how hazards might occur.
Key Actions:
- List All Possible Hazards: Identify biological (e.g., bacteria, viruses), chemical (e.g., pesticides, allergens), and physical hazards (e.g., foreign objects) that could affect food safety.
- Analyze Each Stage of Production: Examine each step of the food production process—from raw material sourcing to final product delivery—to identify where hazards might be introduced.
- Use Historical Data: Leverage past data on contamination events and recalls to identify recurring hazards.
- Consult Regulatory Guidelines: Ensure that all identified hazards comply with local and international food safety regulations and standards.
Step 2: Risk Assessment Matrix
The risk assessment matrix is a significant tool in the analysis of identified hazards against their likelihood and potential impact. This step will allow the prioritization of risks and further control of efforts towards them.
Key Actions:
- Assess Likelihood and Severity: Estimate the probability of occurrence of every hazard and the seriousness of its potential impact on public health.
- Create a Risk Matrix: Plot the hazards on a matrix with likelihood on one axis and severity on the other. This is usually a very useful, visual tool to help prioritize risks because of their overall threat level.
- Prioritize Hazards: The highest quality attention and mitigation should be focused on high likelihood and high severity hazards.
- Document Findings: The risk matrix and the reasons for the prioritization of hazards are well documented.
Step 3: Implementing Control Measures
In turn, control measure development and implementation follow after the hazards have been prioritized. Effective control measures are those specifically targeted to the hazard and context of operations.
Key Actions:
- Develop Control Strategies: Design measures to prevent, eliminate, or reduce hazards to an acceptable level.
- Implement Controls: Apply the designed strategies in practice in all stages of the production process that are applicable.
- Staff Training: Ensure all staff have been trained for the new measures on control, and everyone knows his role and how to play it towards maintaining food safety.
- Verify Effectiveness: Conduct trial runs and initial tests to check whether the control measures have been effective in mitigating the identified hazards.
Step 4: Monitoring and Review
This involves continuous monitoring and regular reviews to ensure that control measures remain effective, and any potential new risks are recognized and managed in a timely manner.
Key Actions:
- Establish Monitoring Procedures: Develop procedures to regularly monitor critical control points. This includes routine inspections, sampling, and testing.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Perform periodic audits to verify compliance with food safety protocols and to identify areas for improvement.
- Review and Update Risk Assessments: Regularly review and update the risk assessment to incorporate new data, emerging risks, and changes in production processes.
- Document and Report: Maintain detailed records of monitoring activities, audit findings, and any corrective actions taken. Transparent documentation supports traceability and compliance.
By following these steps, industry leaders can conduct thorough and effective food safety risk assessments, ensuring the safety and integrity of their food products while complying with regulatory standards.
Case Study: AI-Powered Risk Assessment with SGS Digicomply
SGS Digicomply innovates food safety risk assessment by empowering it with artificial intelligence. Underpinned by thousands of data sources, AI technology enables the deepest and most targeted screening of food safety data and key insights. Contextualizing these insights with real-time laboratory data, it allows for the identification and connection of emerging risks previously unseen.
Key Features of SGS Digicomply:
- Comprehensive Hazard Analysis and Preventive Control: AI makes sure that hazard analysis and preventive control are effectively carried out to reduce food safety risks.
- Regulation monitoring: It opens up over 150,000 regulations across more than 150 countries to ensure that businesses stay ahead of changes in regulatory compliance.
- incident monitoring: Kept updated with alerts and recalls issued by more than 70 government bodies, further augmented by news journals and insights of industry associations.
- Scientific Analyses: More than 2 million documents from scientific, government, and industry-leading sources to keep businesses abreast of the latest research and technological developments.
- Social Media and News Tracking: Monitoring media discussions, social networks such as Twitter, and NGO influencers for capturing public sentiment and detecting emerging trends.
- Insights from SGS Labs: Tapping into data from SGS Labs, which analyze billions of data points to provide real-time laboratory analysis and predictions.
SGS Digicomply tools can integrate the whole process—from data collection at the very initial phase to actionable insights. A company will have the capability to track effectively, analyze, and act on trends and risks in the food sector. Stay ahead in regulatory changes and anticipate possible risks; seize new opportunities that keep you innovating for sustainable development.
Cover the Entire Process: From Risk Identification to Actionable Insights
From the identification of the first risks to the formulation of an action-oriented output, SGS Digicomply's tools have an integrated and seamless process. It enables organizations to track effectively the food safety risks faced by the industry, analyze them, and respond to them.
First, there is an extended data collection, capturing all types of data signals from various sources. The early warning phase identifies critical issues and enriches them with experts' knowledge. This finally allows the realization of insights to take place, allowing organizations to make proper decisions and implement strategic actions on time.
Using AI-based solutions from SGS Digicomply, the companies will be able to pre-act on regulatory change, anticipate risks, and first leverage opportunities. This holistic approach ensures that risk management is boosted and innovation and sustainable development are seen in the food industry.
Explore Our Food Safety Intelligence Hub Demo
By combining thousands of data sources, AI technology enables the most comprehensive and targeted screening of food safety data and key insights. These insights are contextualized with real-time laboratory data, allowing for the identification and connection of emerging risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is food safety risk assessment?
-
Food safety risk assessment is a systematic process used to identify, evaluate, and manage potential hazards associated with food safety. This process involves hazard identification, risk analysis, implementation of control measures, and continuous monitoring to ensure food products are safe for consumption and comply with regulatory standards.
- How is risk assessment in the food industry conducted?
-
Risk assessment in the food industry involves several steps: preparing for the assessment, identifying potential hazards, evaluating risks using a risk assessment matrix, implementing control measures to mitigate identified risks, and continuously monitoring and reviewing the effectiveness of these measures. The goal is to ensure food safety and prevent foodborne illnesses.
- What is the purpose of food safety risk analysis?
-
The purpose of food safety risk analysis is to systematically evaluate potential hazards that could compromise food safety. This process helps prioritize risks based on their likelihood and severity, allowing food industry professionals to focus on mitigating the most significant threats. Effective risk analysis supports proactive management of food safety risks.
- Can you provide a food safety risk assessment example?
-
Certainly! One common food safety risk assessment example involves assessing the risk of Salmonella contamination in poultry. This process includes identifying potential contamination sources such as feed and water, evaluating the likelihood and impact of contamination, implementing control measures like strict hygiene practices and vaccination programs, and continuously monitoring for effectiveness.
- How do you create a food safety risk assessment matrix?
-
Creating a food safety risk assessment matrix involves plotting identified hazards on a grid with two axes: likelihood of occurrence and severity of impact. Each hazard is evaluated and placed on the matrix, which helps prioritize risks. High-likelihood and high-severity hazards are given top priority for control measures. This visual tool aids in making informed decisions about risk management.
- What is an HACCP food safety risk assessment example?
-
An example of an HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) food safety risk assessment is evaluating the risk of Listeria contamination in ready-to-eat foods. This involves identifying critical control points in the production process where contamination could occur, such as during processing and storage. Control measures like temperature control, surface sanitation, and regular microbial testing are then implemented to mitigate the risk.





.webp?width=1644&height=1254&name=Food%20Safety%20Dashboard%201%20(1).webp)
