Ground beef is a staple in households and restaurants alike, widely used in dishes ranging from hamburgers to tacos. However, the handling and processing of ground beef pose unique safety challenges, as it is particularly susceptible to contamination. Ground beef recalls are a common response to the detection of foodborne pathogens like E. coli, Salmonella, and Listeria, or to other safety risks, such as mislabeling or the presence of foreign materials. This guide provides an in-depth look at the causes of ground beef recalls, the regulatory framework governing these recalls, and the preventive measures that producers and suppliers can adopt to ensure safe, high-quality products. Let's dive into this type of Food Recall.
What is a Ground Beef Recall?
A ground beef recall is the process of removing potentially unsafe or contaminated ground beef products from the market. Recalls can be voluntary—initiated by manufacturers when a risk is detected—or mandated by regulatory authorities such as the U.S. Department of Agriculture's Food Safety and Inspection Service (USDA FSIS). The goal of a recall is to protect consumers from products that could lead to illness or injury and to prevent a small issue from escalating into a larger public health crisis.
Ground beef recalls can involve various types of products, including packaged ground beef, pre-formed burger patties, and ground beef-based ready-to-eat items. Given the potential risks associated with contamination, recalls are handled with urgency and require strict compliance with food safety regulations.
Main Causes and Hazards of Ground Beef Recalls
Several factors contribute to ground beef recalls, each posing significant risks to consumers:
-
Microbial Contamination: Pathogens like Escherichia coli (E. coli), Salmonella, and Listeria monocytogenes are common causes of ground beef recalls. Contamination often occurs during slaughter or processing and can be exacerbated by improper handling or cross-contamination in facilities. E. coli O157
, in particular, is a highly dangerous strain that can cause severe illness and, in some cases, lead to kidney failure or death. -
Undeclared Allergens: Although uncommon in ground beef, undeclared allergens can occur when processing facilities handle multiple products and cross-contamination happens. For instance, if ground beef is processed in an environment where dairy or soy-based products are also handled, traces of these allergens may unintentionally end up in the beef, posing a serious risk to those with allergies.
-
Foreign Materials: Physical contaminants, such as metal fragments, plastic pieces, or bone shards, sometimes find their way into ground beef products. These foreign materials can result from equipment malfunctions, poor handling practices, or inadequate quality checks, creating choking hazards or the risk of internal injury for consumers.
-
Improper Labeling: Labeling errors can lead to recalls if critical information, such as fat content or allergen warnings, is omitted or misrepresented. While mislabeling is less likely to cause direct harm, it can undermine consumer trust and regulatory compliance, especially if the label does not reflect the product’s true contents.
Understanding these hazards is essential for preventing ground beef recalls and ensuring consumer safety. Each cause underscores the importance of rigorous quality control, sanitation, and handling protocols throughout the production process.
Regulatory Authorities' Role in Ground Beef Recalls
In the United States, ground beef recalls are primarily overseen by the USDA FSIS. This agency is responsible for inspecting meat and poultry products, enforcing safety standards, and managing recalls when potential risks are identified. Key responsibilities of regulatory authorities in ground beef recalls include:
-
Inspection and Surveillance: The USDA FSIS conducts routine inspections of meat processing facilities to verify compliance with safety regulations. They also test samples for pathogens and other contaminants, helping to detect issues before they reach consumers.
-
Classification of Recalls: When a recall is necessary, FSIS classifies it based on the severity of the risk:
- Class I Recall: High risk, involving products that could cause serious health consequences or death. Most microbial contamination recalls fall under this category.
- Class II Recall: Moderate risk, where exposure to the product may cause temporary health issues but is unlikely to lead to severe illness.
- Class III Recall: Low risk, involving products that violate labeling or regulatory requirements without posing direct health risks.
-
Recall Management and Oversight: FSIS collaborates with companies to develop a recall strategy, track the distribution of affected products, and monitor the effectiveness of the recall. The agency also reviews companies' corrective actions to prevent future incidents.
-
Public Notification: FSIS issues public notices for all recalls, informing consumers, retailers, and distributors of affected products. Public awareness is crucial for preventing consumption of recalled items and minimizing health risks.
-
Post-Recall Assessment: After a recall is completed, FSIS evaluates the company’s response and may require additional corrective actions, such as improving sanitation procedures or enhancing traceability systems, to prevent recurrence.
The USDA FSIS’s involvement ensures that ground beef recalls are handled efficiently and transparently, reinforcing consumer trust and maintaining food safety standards.
Impact of Ground Beef Recalls on the Industry
Ground beef recalls can have significant consequences for producers, processors, and retailers, affecting various aspects of their business:
-
Financial Losses: The direct costs of removing products, conducting additional testing, and implementing corrective measures can be substantial. Indirect costs, such as lost sales, reduced market share, and potential legal liabilities, add to the financial burden.
-
Damage to Brand Reputation: Recalls, particularly those involving high-profile pathogens like E. coli, can erode consumer trust. Negative publicity may lead to long-term reputation damage, impacting future sales and customer loyalty.
-
Increased Regulatory Scrutiny: Following a recall, companies often face closer monitoring from FSIS, including more frequent inspections, additional reporting requirements, and potential fines for non-compliance.
-
Supply Chain Disruption: Recalls disrupt the entire supply chain, affecting relationships with suppliers, distributors, and retailers. Companies may need to adjust contracts, renegotiate terms, and strengthen quality control measures to restore operations.
Understanding these impacts underscores the importance of maintaining strict safety and quality standards to prevent recalls and mitigate their effects on business operations.
Preventive Measures for Ground Beef Recalls
Preventing ground beef recalls requires a proactive approach to food safety. Key preventive measures include:
-
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) Implementation: HACCP plans are essential for identifying potential hazards and establishing controls to prevent contamination. A well-executed HACCP plan addresses every stage of processing, from slaughter to packaging.
-
Supplier Verification: Working with trusted suppliers and conducting regular audits ensures that raw materials meet safety standards, reducing the risk of contamination before processing begins.
-
Sanitation Protocols and Cross-Contamination Prevention: Strict sanitation protocols in processing facilities help prevent microbial contamination. Additionally, measures to prevent cross-contamination—such as designated equipment for allergen-free processing—are essential in ensuring product safety.
-
Regular Testing and Quality Control: Routine testing for pathogens, foreign materials, and allergens helps catch potential issues before products reach the market. Advanced technology, such as metal detectors and microbial testing, can enhance quality control.
-
Traceability Systems: Implementing traceability technology, like barcoding and digital tracking, improves recall efficiency by allowing companies to quickly identify and locate affected batches.
-
Employee Training: Ensuring that employees are well-trained in food safety protocols, including proper handling, sanitation, and labeling practices, minimizes the risk of human error and contamination.
By adopting these preventive practices, companies can reduce the likelihood of ground beef recalls, protecting both their brand and their consumers.
Conclusion
Ground beef recalls are a vital aspect of food safety management, as they protect consumers from potentially dangerous products while maintaining public trust in the food supply. Understanding the causes of ground beef recalls—such as microbial contamination, foreign materials, and labeling issues—and the role of regulatory authorities provides industry professionals with insights needed to manage and prevent these events effectively.
For companies in the ground beef industry, proactive safety measures are essential. Implementing HACCP plans, ensuring rigorous sanitation and quality control, and investing in traceability systems are all critical for minimizing risks. Through close collaboration with regulatory authorities like the USDA FSIS and adherence to best practices, ground beef producers and processors can navigate recalls responsibly, uphold safety standards, and continue to deliver safe products to consumers.
Last Month's Food Recalls and Safety Incidents
Explore the latest food recalls, market withdrawals, and safety alerts in our free Food Safety Incidents Dashboard. Updated monthly and powered by SGS Digicomply, this dashboard provides a clear, filterable list of last month’s global food recalls and incidents, allowing you to stay informed on the products and hazards affecting the industry.

How manufacturers and companies can track and utilize global recall data:
SGS Digicomply continuously monitors and analyzes millions of data sources across over 160 jurisdictions. With easy-to-use filters for sources, locations, products, substances, hazards, and more, our platform allows manufacturers to track recall trends and gain actionable insights powered by AI-Copilot.
Explore our interactive demos to see these tools in action.
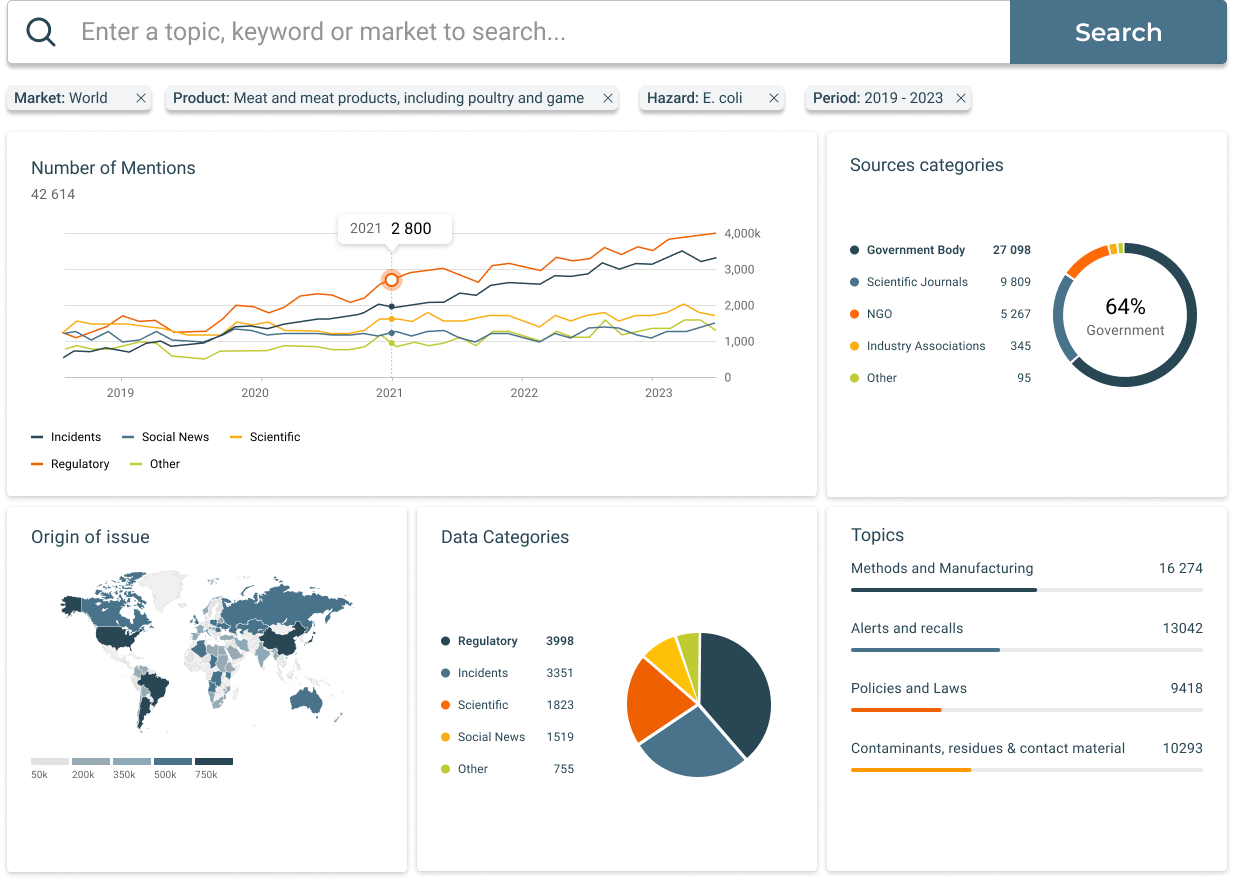
By combining diverse data sources, SGS Digicomply offers the most comprehensive and targeted screening of food safety data, contextualized with real-time lab data to identify emerging risks.





.webp?width=1644&height=1254&name=Food%20Safety%20Dashboard%201%20(1).webp)
