In recent findings by the OCU, the presence of arsenic in rice has raised significant concerns. Arsenic, a carcinogenic, liver-damaging, and neurotoxic heavy metal, is listed by the WHO as one of the ten most toxic substances affecting public health. While the levels detected in the rice analyzed by the OCU fall within the European Union's safety standards, the accumulation of arsenic in the body over time calls for caution.
Understanding the Risk of Arsenic in Rice
Arsenic infiltrates rice through natural and artificial irrigation processes, originating from both natural sources and human contamination. The OCU report suggests that individuals with diets heavily reliant on rice may face health implications due to the cumulative nature of arsenic intake. This situation mirrors the cautionary approach taken with other toxins like mercury found in certain fish varieties.
Assessing Safe Consumption Levels
The European Food Safety Agency (EFSA) defines a maximum threshold of 0.3 μg of arsenic per kg of body weight per day. However, it is crucial to consider individual body weight, especially for children, adolescents, and individuals with lower body mass. For instance, a 6-month-old infant weighing around 8 kg could surpass the safety limit by consuming two servings of instant cereal porridge with rice daily.
Varietal Disparities in Arsenic Content: What You Need to Know
Analysis of 136 rice samples revealed varying arsenic concentrations across different varieties and derived products. Brown rice and rice-based pancakes exhibited the highest levels of the toxin. In contrast, short-grain white rice and puffed rice cereals contained comparatively lower amounts. Pre-cooked rice and long-grain varieties demonstrated even lower arsenic levels, with vaporized rice falling in between. Additionally, trace amounts of arsenic were found in rice noodles and breakfast cereals.
Recommendations and Precautions for Arsenic in Rice
Considering the potential health risks associated with arsenic consumption, consumer associations advocate for increased monitoring and controls to accurately detect and regulate arsenic levels in the market. Opting for rice varieties from regions with higher safety standards, such as Spanish or European Union-grown rice, is advised. In specific population segments, like individuals with celiac disease or infants transitioning to solid foods, alternative grains like barley or oats are recommended to mitigate potential neurological effects from arsenic accumulation.
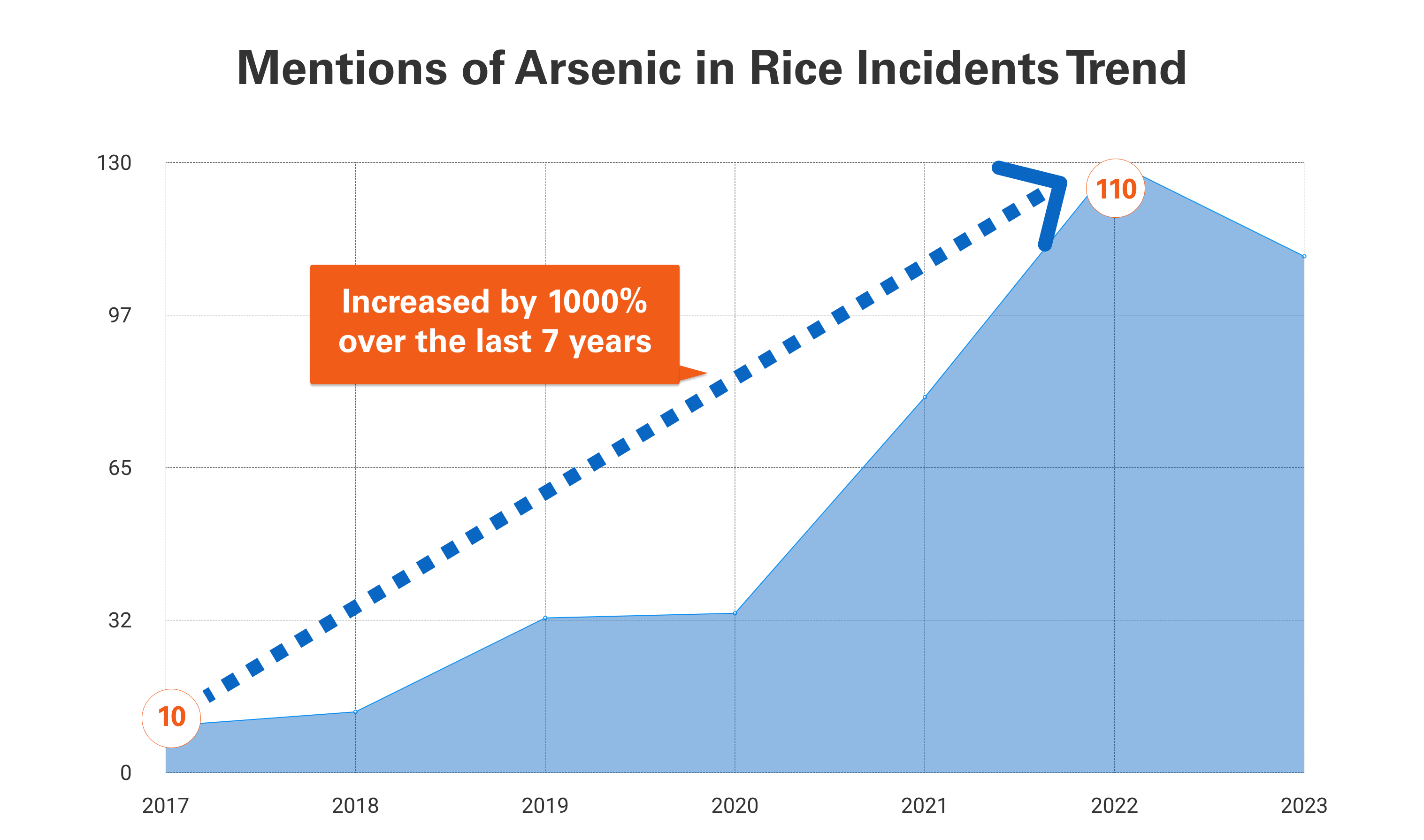
Arsenic in Rice: SGS Digicomply Food Safety Snapshot
Examining the chart "Mentions of Arsenic in Rice Incidents Trend" sourced from Digicomply APP, which starkly indicates a 1000% surge in incidents over the past seven years, we are confronted with a deeply concerning trajectory. This underscores a pressing safety concern surrounding arsenic levels in rice.
Given this concerning trend, there is an urgent need to amplify control and regulation of arsenic levels within the rice market. The recommendation to opt for rice varieties from regions with elevated safety standards becomes significantly more pertinent in light of this data. Moreover, for sensitive population segments like individuals with celiac disease or infants transitioning to solid foods, the shift towards alternative grains like barley or oats stands as a critical measure in alleviating potential neurological impacts stemming from arsenic accumulation.
Conclusion
While rice remains a dietary staple for many, it is imperative to approach consumption with mindfulness. Balancing the intake of rice with a diverse range of foods helps minimize potential excesses. Implementing simple home-cooking techniques, like pre-soaking and thorough washing, can significantly reduce arsenic levels. By adopting a holistic approach to nutrition, we can mitigate the impact of contaminants and ensure a safe, well-rounded diet. Explore SGS Digicomply platform now.





.webp?width=1644&height=1254&name=Food%20Safety%20Dashboard%201%20(1).webp)
