Food fraud vulnerability assessment is simply a process used in the identification and mitigation of associated risks with fraudulent activities in the supply chain. This would hence involve assessment of the food products for their potential susceptibility to fraud and strategizing on measures of prevention. Thus, giving the backbone to assurance of food safety, consumer health protection, and brand integrity protection. By understanding and addressing vulnerabilities, businesses can better safeguard their products and reduce the economic impact of food fraud.
Understanding Food Fraud Vulnerability
Food fraud vulnerability is the state wherein certain food products are found vulnerable to the basic types of fraudulent activities, such as adulteration, substitution, mislabeling, and counterfeiting. Several drivers act together to present the food system with vulnerability to food fraud. These drivers are enumerated below:
- Economic Drivers: High-value products and ingredients pose a greater risk of becoming targets for fraud since the potential financial gain is huge in their case. It is the economic pressures that may motivate fraudulent practices.
- Supply Chain Complexity: Longer and more complex the supply chains, the greater the risks of fraud, since products go through many hands and are therefore difficult to trace and validate for authenticity.
- Gaps in Regulations: Different regulations concerning different areas provide the opportunity for fraudsters to exploit their fraud through the weak links in the legal system.
The knowledge of these very factors is the real trick in effectively ascerting and reducing food fraud vulnerabilities.
Steps to Conduct a Food Fraud Vulnerability Assessment
The steps to be taken to identify, assess, and mitigate the risks include:
Step 1: Identify Potential Hazards
Identify what kind of problems involving food fraud may have an impact on your products. Common forms of food fraud include but are not limited to the following: adulteration, substitution, mislabeling, or counterfeiting.
Step 2: Assess the Likelihood of Occurrence
For every identified hazard, determine the likelihood of occurrence. This would factor in a trend of events through historical data, an analysis of economic incentive, and analysis of the transparency of your supply chain. Consider factors such as past incidents, the financial value of the products, and a number of intermediaries within the supply chain.
Step 3: Evaluate the Potential Impact
Determine what may come out of each hazard identified. From health risks to consumers to economic losses for your business and possible reputation damage of your brand, such risks should be first in line and prioritized for immediate actions.
Step 4: Prioritize Vulnerabilities
Rank in order, from highest to lowest, the vulnerabilities identified in terms of probability of occurrence and probable impact. This will help to focus efforts and resources on high-level risks. The risk matrix or scoring system will classify these vulnerabilities into high, medium, or low priority.
Step 5: Develop Mitigation Strategies
Design and implement mitigation strategies for high-priority vulnerabilities, which may involve the following:
- Controls: Stringent quality control and test processes should be put in place.
- Improved Traceability: From farm to table, or the various supply chain stages of ingredients and products, traceability through blockchain technology development.
- Improved Supplier Relationships: Deeper supplier audits and transparency in collaboration.
The above steps let companies detect and handle their food fraud vulnerabilities in an orderly way, thus capable of taking measures to raise the safety and integrity of food products.
Tools and Techniques for Vulnerability Assessment
Use of AI and Data Analytics
An important role in the examination of food fraud vulnerability assessment is played by AI and data analytics. In most cases, huge data can be gone through to come up with a particular pattern that is giving rise to some anomalies, thus indicating fraud risk. The machine learning algorithms have a historical view of past experiences and economic trends to predict the potential to have new incidents of fraud.
Role of Blockchain in Enhancing Traceability
Blockchain technology allows for transparency and security in tracing products right along the supply chain. The transactions are recorded on an immutable ledger, making it difficult for fraudsters to change any record without being detected. Improved traceability contributes to ensuring the authenticity of ingredients and products.
Risk Assessment Frameworks and Software Tools
There are different frameworks and software tools that can be adapted to carry out food fraud vulnerability assessments. These tools could be applied in the systematic evaluation of business risks and the corresponding mitigation measures. Examples are:
- Vulnerability Assessment and Critical Control Points (VACCP): A framework specifically designed to address food fraud.
- Food Fraud Vulnerability Assessment (FFVA) Tools: Software solutions that provide structured methodologies for assessing and managing food fraud risks.
This fact allows the application of these tools and techniques to make an effective and detailed food fraud vulnerability assessment.
Identifying and Mitigating Food Fraud Vulnerabilities with SGS Digicomply
SGS Digicomply leverages advanced AI-driven tools to enhance food fraud vulnerability assessments. By integrating comprehensive data analysis and predictive technologies, SGS Digicomply helps businesses identify and mitigate risks effectively.
Food Safety Intelligence Hub
The Food Safety Intelligence Hub aggregates global food safety data, allowing for real-time monitoring and analysis. AI algorithms detect patterns and anomalies that could indicate potential fraud risks, enabling proactive measures. Watch demo.
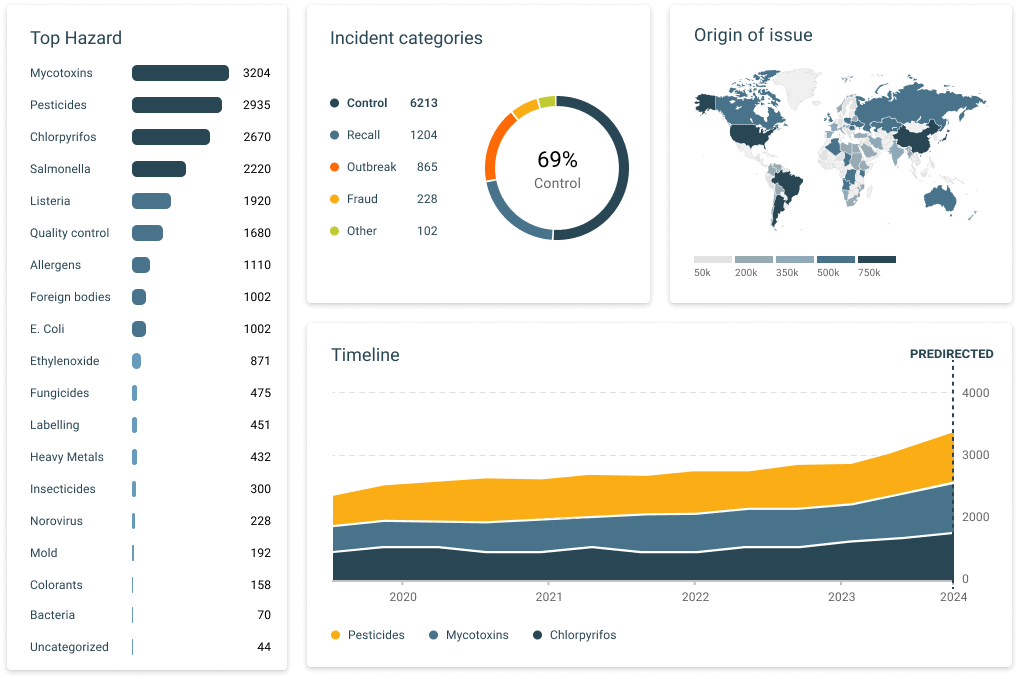
Regulatory Intelligence Hub
The Regulatory Intelligence Hub ensures compliance by continuously monitoring global regulatory changes. It helps identify vulnerabilities related to regulatory gaps and provides insights into maintaining alignment with current laws. Watch demo.

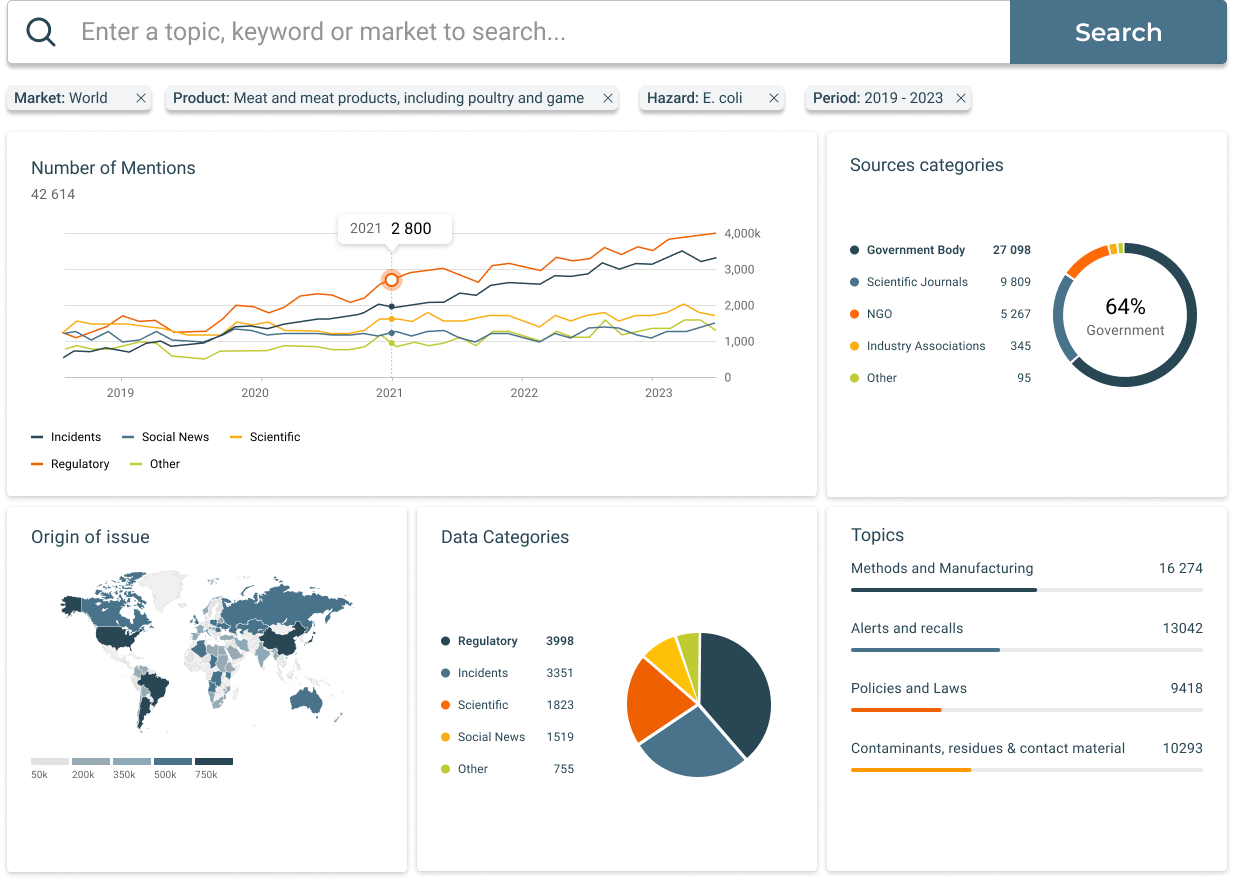
Global Ingredient Monitor
This tool tracks ingredient authenticity and quality throughout the supply chain. AI-driven analysis detects adulteration and substitution, ensuring ingredient integrity and reducing fraud risk. Watch demo.

Horizon Scanning
Horizon Scanning uses AI to predict emerging fraud threats by analyzing global data sources. This proactive approach offers early warnings and trend analyses, helping businesses stay ahead of potential risks. Watch demo.
SGS Digicomply’s suite of AI-powered tools provides a comprehensive approach to food fraud vulnerability assessment. By leveraging these technologies, businesses can enhance traceability, ensure regulatory compliance, and proactively mitigate fraud risks.




.webp?width=1644&height=1254&name=Food%20Safety%20Dashboard%201%20(1).webp)
