Cheese recalls due to Listeria monocytogenes outbreaks are a significant concern in the dairy industry and among consumers. Listeria is a particularly dangerous pathogen that can thrive in refrigerated environments and pose severe health risks, especially to vulnerable populations such as pregnant women, infants, the elderly, and individuals with compromised immune systems. When Listeria is detected in cheese products, recalls are initiated to prevent outbreaks and protect public health. This guide covers the causes of Listeria outbreaks in cheese, the recall process, regulatory oversight, and essential preventive measures to ensure food safety. Let's dive into this type of Food Recall.
What is a Listeria Outbreak Cheese Recall?
A Listeria outbreak cheese recall is the urgent removal of potentially contaminated cheese products from the market due to the presence of Listeria monocytogenes, a bacterium known to cause serious foodborne illness. Recalls are often initiated voluntarily by manufacturers when contamination is detected but can also be mandated by regulatory authorities like the FDA. The main objective of a Listeria cheese recall is to protect consumers from potential health risks, as Listeria infections can lead to severe illnesses, including listeriosis, which is particularly harmful to certain at-risk groups.
Recalls related to Listeria typically involve soft cheeses, such as Brie, Camembert, queso fresco, and blue cheese, due to their high moisture content and pH levels, which provide an ideal environment for Listeria growth. Preventing contamination at every stage, from milk production to cheese processing and packaging, is critical to avoid recalls.
Main Causes and Hazards of Listeria Outbreak Cheese Recalls
The following are the most common causes and hazards associated with Listeria contamination in cheese products:
-
Inadequate Sanitation Practices: Listeria can survive in processing facilities, especially in cold, damp environments. Contaminated surfaces, equipment, or packaging areas can easily transfer Listeria to cheese during production if proper sanitation is not maintained.
-
Cross-Contamination in Processing Facilities: When different types of cheese or other foods are processed in the same facility, there is a risk of cross-contamination if strict separation and cleaning protocols are not followed. Listeria can spread between equipment and products, especially in facilities where other Listeria-prone foods are handled.
-
Environmental Contamination: Listeria is commonly found in soil and water, which can lead to contamination of raw milk used in cheese production. Using contaminated water in processing or improper handling of raw milk increases the risk of Listeria entering the production chain.
-
Cold Storage Contamination: Unlike many pathogens, Listeria can thrive in refrigerated environments. Cheese stored in cold storage is particularly at risk if facilities are not regularly cleaned and maintained to prevent bacterial growth.
Understanding these hazards is critical for cheese producers, as effective control measures throughout the supply chain are essential to prevent contamination and avoid costly recalls.
Regulatory Authorities' Role in Listeria Cheese Recalls
The FDA and CDC play pivotal roles in managing Listeria cheese recalls in the United States. Their responsibilities include:
-
Inspection and Monitoring: The FDA inspects cheese production facilities to ensure compliance with safety regulations, focusing on sanitation practices, equipment maintenance, and environmental controls to prevent Listeria growth.
-
Testing and Surveillance: The FDA conducts regular testing of cheese products, both domestically produced and imported, to detect the presence of Listeria. This proactive approach helps identify contaminated products before they reach consumers.
-
Recall Classification and Management: When a recall is necessary, the FDA classifies it based on health risks:
- Class I Recall: High risk, involving products that could lead to severe health issues or death, especially in the case of Listeria contamination.
- Class II Recall: Moderate risk, where exposure may cause temporary or reversible health issues.
- Class III Recall: Low risk, involving regulatory violations without immediate health threats.
-
Public Notification: The FDA and CDC issue public alerts for Class I and Class II recalls, providing details on the affected products, lot numbers, and health risks. These notifications are disseminated via press releases, social media, and official websites to inform consumers.
-
Follow-Up and Corrective Actions: After a recall, regulatory authorities may require manufacturers to implement corrective actions, such as revising sanitation protocols or upgrading equipment, to prevent future contamination incidents.
The involvement of regulatory authorities ensures that Listeria cheese recalls are managed effectively, protecting public health and maintaining transparency within the food industry.
Impact of Listeria Cheese Recalls on the Industry
Listeria cheese recalls can have significant repercussions for manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. Key impacts include:
-
Financial Losses: The costs associated with removing contaminated products, conducting extensive testing, and implementing corrective actions can be substantial. Additional expenses may arise from legal liabilities, lost sales, and potential compensation claims from affected consumers.
-
Reputation Damage: Cheese recalls due to Listeria outbreaks can erode consumer trust, as Listeria contamination is widely regarded as a severe food safety issue. Rebuilding brand reputation requires time, transparency, and a commitment to improved safety practices.
-
Stricter Regulatory Scrutiny: Following a recall, companies may face increased monitoring and more frequent inspections from regulatory authorities, adding to compliance costs and requiring ongoing improvements to meet safety standards.
-
Supply Chain Disruption: Cheese recalls disrupt the entire supply chain, affecting raw milk suppliers, processing facilities, and retailers. Effective coordination with suppliers and distributors is essential to restore normal operations and reassure consumers of product safety.
Understanding these impacts highlights the importance of implementing preventive measures and maintaining high standards of food safety throughout the cheese production process.
Preventive Measures for Listeria Cheese Recalls
Preventing Listeria cheese recalls requires a proactive approach to food safety, particularly in production, storage, and handling. Key preventive measures include:
-
Enhanced Sanitation Protocols: Implementing rigorous sanitation practices in cheese processing facilities is essential to prevent Listeria contamination. This includes regularly cleaning and sanitizing all equipment, tools, and surfaces and ensuring that employees follow strict hygiene protocols.
-
Regular Environmental Testing: Conducting environmental testing for Listeria in processing areas helps detect potential contamination sources. Regular swabbing of surfaces, drains, and equipment allows for early identification of Listeria hotspots and enables prompt corrective actions.
-
Cold Chain Management: Since Listeria can thrive in refrigerated environments, maintaining proper cold storage conditions is critical. Regular monitoring and cleaning of refrigeration units, storage rooms, and cooling equipment prevent bacterial growth.
-
Employee Training: Educating employees on food safety practices, including proper handling, sanitation, and hygiene protocols, reduces the risk of contamination due to human error. Well-trained staff are essential for maintaining consistent safety standards.
-
Supplier Verification and Quality Control: Working with trusted suppliers and verifying the quality of raw milk reduces the risk of Listeria contamination at the source. Quality control measures, including regular testing of raw ingredients, help identify potential risks before they enter the production process.
-
Separation of Production Zones: Implementing strict separation between raw and finished products minimizes the risk of cross-contamination. Designating specific equipment and areas for different stages of production helps maintain a controlled environment.
By incorporating these preventive practices, cheese producers can reduce the likelihood of Listeria contamination, safeguard consumer health, and maintain regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
Listeria outbreaks in cheese products are a serious public health concern that requires swift and effective recall management. Understanding the main causes of contamination—such as inadequate sanitation, environmental factors, and cross-contamination—enables industry professionals to take preventive measures and uphold food safety standards.
For cheese manufacturers, the key to successful recall management lies in proactive safety practices, including enhanced sanitation protocols, regular testing, and thorough employee training. By adhering to regulatory guidelines and working closely with the FDA, cheese producers can ensure that their products meet safety standards and minimize the risk of Listeria outbreaks.
Through transparent communication, rigorous quality control, and a commitment to continuous improvement, the cheese industry can protect both its consumers and its reputation, contributing to a safer and more reliable food supply.
Last Month's Food Recalls and Safety Incidents
Explore the latest food recalls, market withdrawals, and safety alerts in our free Food Safety Incidents Dashboard. Updated monthly and powered by SGS Digicomply, this dashboard provides a clear, filterable list of last month’s global food recalls and incidents, allowing you to stay informed on the products and hazards affecting the industry.

How manufacturers and companies can track and utilize global recall data:
SGS Digicomply continuously monitors and analyzes millions of data sources across over 160 jurisdictions. With easy-to-use filters for sources, locations, products, substances, hazards, and more, our platform allows manufacturers to track recall trends and gain actionable insights powered by AI-Copilot.
Explore our interactive demos to see these tools in action.
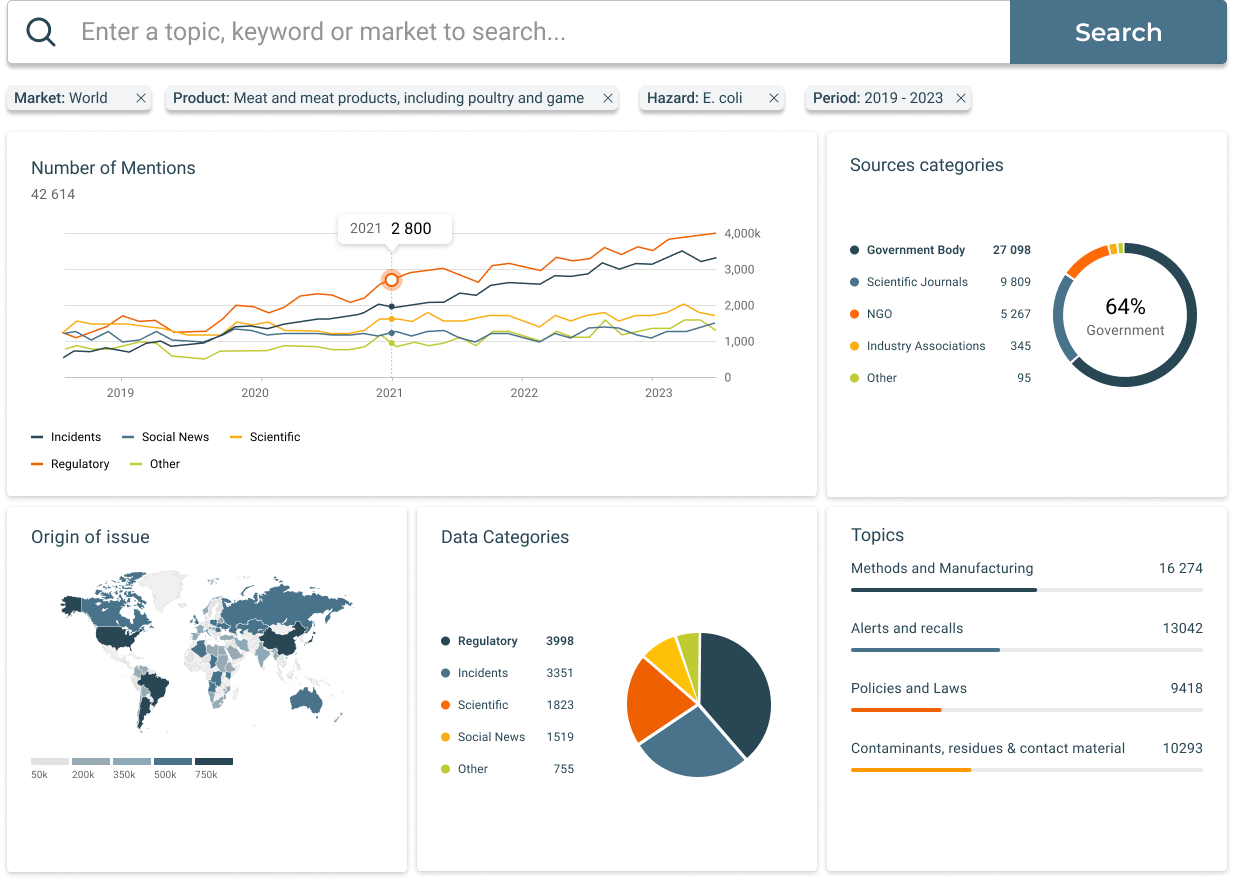
By combining diverse data sources, SGS Digicomply offers the most comprehensive and targeted screening of food safety data, contextualized with real-time lab data to identify emerging risks.





.webp?width=1644&height=1254&name=Food%20Safety%20Dashboard%201%20(1).webp)
