Vegetables are a vital part of a healthy diet and are consumed globally in a wide variety of forms. However, due to their natural growth environments and handling throughout production, vegetables are susceptible to contamination, which can lead to recalls. A vegetable recall is often initiated when a product is found to carry harmful pathogens, such as Salmonella, Listeria, or E. coli, or when foreign materials or mislabeling issues are detected. This guide delves into the causes of vegetable recalls, regulatory oversight, their impact on the produce industry, and the preventive measures essential for safe vegetable production and distribution. Let's dive into this type of Food Recall.
What is a Vegetable Recall?
A vegetable recall is the process of removing contaminated or otherwise unsafe vegetables from the market. Recalls may be initiated voluntarily by growers and producers or required by regulatory bodies like the FDA if a health risk is identified. Vegetable recalls can affect a variety of produce, including leafy greens, root vegetables, packaged salads, and pre-cut vegetable mixes. Given that many vegetables are consumed raw or minimally processed, recalls are handled urgently to prevent potential outbreaks of foodborne illness.
Main Causes and Hazards of Vegetable Recalls
Vegetable recalls generally result from several specific hazards, each posing unique risks to consumer health:
-
Bacterial Contamination (e.g., Salmonella, Listeria, E. coli): Bacterial pathogens are one of the primary causes of vegetable recalls. Salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes, and E. coli can contaminate vegetables during growth, harvest, or handling. Leafy greens, such as spinach and lettuce, are particularly prone to contamination as they are often eaten raw, making them a high-risk food for bacterial infection.
-
Environmental Contaminants: Because vegetables are grown outdoors, they are exposed to environmental contaminants such as polluted irrigation water, animal intrusion, or soil-borne bacteria. Proper monitoring of water quality and field conditions is essential to mitigate these risks.
-
Foreign Material Contamination (e.g., Plastic, Metal, Stones): Foreign materials like plastic fragments, metal pieces, or stones can occasionally end up in vegetable products due to equipment issues, packaging errors, or natural factors. These contaminants can cause physical harm to consumers and are a common reason for recalls.
-
Chemical Residues (e.g., Pesticides, Fertilizers): Improper or excessive use of pesticides, fertilizers, or other chemicals can lead to unsafe residue levels on vegetables. If these residues exceed legal limits, they pose health risks and necessitate recalls to protect consumers.
-
Allergen Mislabeling in Processed Vegetables: In the case of packaged or pre-cut vegetable products, cross-contamination with allergens like nuts, soy, or dairy can occur. If these allergens are not properly declared, it poses a risk to individuals with food allergies, leading to recalls to prevent allergic reactions.
Each of these hazards highlights the need for strict quality control, hygiene, and monitoring throughout the vegetable production and distribution process to ensure consumer safety.
Regulatory Authorities' Role in Vegetable Recalls
The FDA oversees vegetable recalls in the United States, with the CDC assisting in managing outbreaks of foodborne illness linked to vegetables. Key roles of regulatory authorities in vegetable recalls include:
-
Inspection and Monitoring: The FDA conducts regular inspections of farms, packing facilities, and distribution centers to ensure compliance with safety standards, focusing on hygiene, water quality, and equipment maintenance to prevent contamination.
-
Testing and Surveillance: The FDA and USDA carry out routine testing and surveillance to detect contaminants in vegetables. These tests are conducted on both raw and processed produce to identify potential risks and prevent contaminated products from reaching consumers.
-
Recall Classification and Management: When a recall is deemed necessary, the FDA classifies it according to health risk:
- Class I Recall: High risk, involving products that could lead to serious health issues or death, such as vegetables contaminated with E. coli or Listeria.
- Class II Recall: Moderate risk, where the product may cause temporary health issues but is unlikely to result in severe illness.
- Class III Recall: Low risk, involving products that violate labeling or regulatory standards without posing immediate health threats.
-
Public Communication and Alerts: When a Class I or Class II recall occurs, the FDA issues public notices detailing affected products, lot numbers, and any potential health risks. This transparent communication helps consumers avoid recalled products.
-
Corrective Actions and Compliance: After a recall, the FDA may require producers to implement corrective actions, such as improving sanitation protocols, monitoring water sources, or enhancing labeling accuracy. These measures help prevent future contamination and support ongoing food safety.
The involvement of regulatory authorities ensures that vegetable recalls are conducted efficiently and transparently, maintaining public health and consumer confidence in the food supply.
Impact of Vegetable Recalls on the Industry
Vegetable recalls can have significant consequences for producers, distributors, and retailers, impacting various aspects of the industry:
-
Financial Losses: Recalls generate direct costs from retrieving products, conducting testing, and implementing corrective actions. Additionally, vegetable recalls often lead to decreased demand, lost sales, and potential legal liabilities if consumers are harmed.
-
Reputation Damage: A vegetable recall, especially one involving high-profile pathogens like E. coli, can damage a brand’s reputation. Rebuilding consumer trust may require transparency, commitment to safety improvements, and effective public relations efforts.
-
Increased Regulatory Scrutiny: Following a recall, companies may face more stringent monitoring from regulatory authorities, including more frequent inspections and heightened compliance requirements. This increased scrutiny can strain resources and affect operations.
-
Supply Chain Disruption: Vegetable recalls impact the entire supply chain, from farmers to retailers. Coordinating effectively with suppliers and distributors is essential to remove affected products, address contamination sources, and restore normal operations.
Understanding these impacts underscores the importance of preventive measures to ensure consumer safety and protect brand reputation.
Preventive Measures for Vegetable Recalls
Preventing vegetable recalls requires proactive safety practices and stringent quality control across all stages of production. Key preventive measures include:
-
Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs): Implementing GAPs on farms ensures that crops are grown, harvested, and handled under safe and hygienic conditions. These practices focus on water quality, soil health, and equipment sanitation to reduce contamination risks.
-
Water Quality Monitoring: Ensuring that irrigation water meets safety standards is essential for vegetable farms. Regular water testing helps identify and mitigate risks associated with contaminated water sources.
-
Routine Microbial Testing: Regular testing for pathogens like E. coli, Salmonella, and Listeria at various stages of production enables early detection of contamination and rapid response.
-
Sanitation and Hygiene Protocols: Following strict sanitation protocols throughout processing and packaging facilities reduces the risk of contamination. Regular cleaning and sanitization of equipment and surfaces are essential for maintaining food safety.
-
Temperature Control and Cold Chain Management: For certain types of vegetables, maintaining proper temperatures during storage and distribution can help prevent spoilage and bacterial growth. Effective cold chain management ensures that perishable vegetables remain safe until they reach consumers.
-
Supplier Verification and Ingredient Testing: Working with trusted suppliers and conducting quality checks on raw and packaged produce ensures that vegetables meet safety standards from the source.
-
Accurate Labeling and Allergen Management: For pre-cut or processed vegetable products, ensuring accurate labeling of ingredients and potential allergens helps prevent mislabeling-related recalls.
By implementing these preventive measures, vegetable producers can reduce the likelihood of recalls, protect consumer health, and maintain regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
Vegetable recalls are essential to protect public health, addressing risks associated with bacterial contamination, foreign materials, and labeling errors. Understanding the causes of vegetable recalls—ranging from microbial hazards to environmental contaminants—enables industry professionals to adopt proactive safety measures that comply with FDA standards.
For vegetable producers, the key to effective recall management lies in prevention. Adhering to GAPs, conducting routine microbial testing, ensuring water quality, and following stringent sanitation protocols are all critical to minimizing contamination risks. Transparent communication with regulatory authorities and the public further reinforces consumer trust and supports a safe, reliable food supply.
Last Month's Food Recalls and Safety Incidents
Explore the latest food recalls, market withdrawals, and safety alerts in our free Food Safety Incidents Dashboard. Updated monthly and powered by SGS Digicomply, this dashboard provides a clear, filterable list of last month’s global food recalls and incidents, allowing you to stay informed on the products and hazards affecting the industry.

How manufacturers and companies can track and utilize global recall data:
SGS Digicomply continuously monitors and analyzes millions of data sources across over 160 jurisdictions. With easy-to-use filters for sources, locations, products, substances, hazards, and more, our platform allows manufacturers to track recall trends and gain actionable insights powered by AI-Copilot.
Explore our interactive demos to see these tools in action.
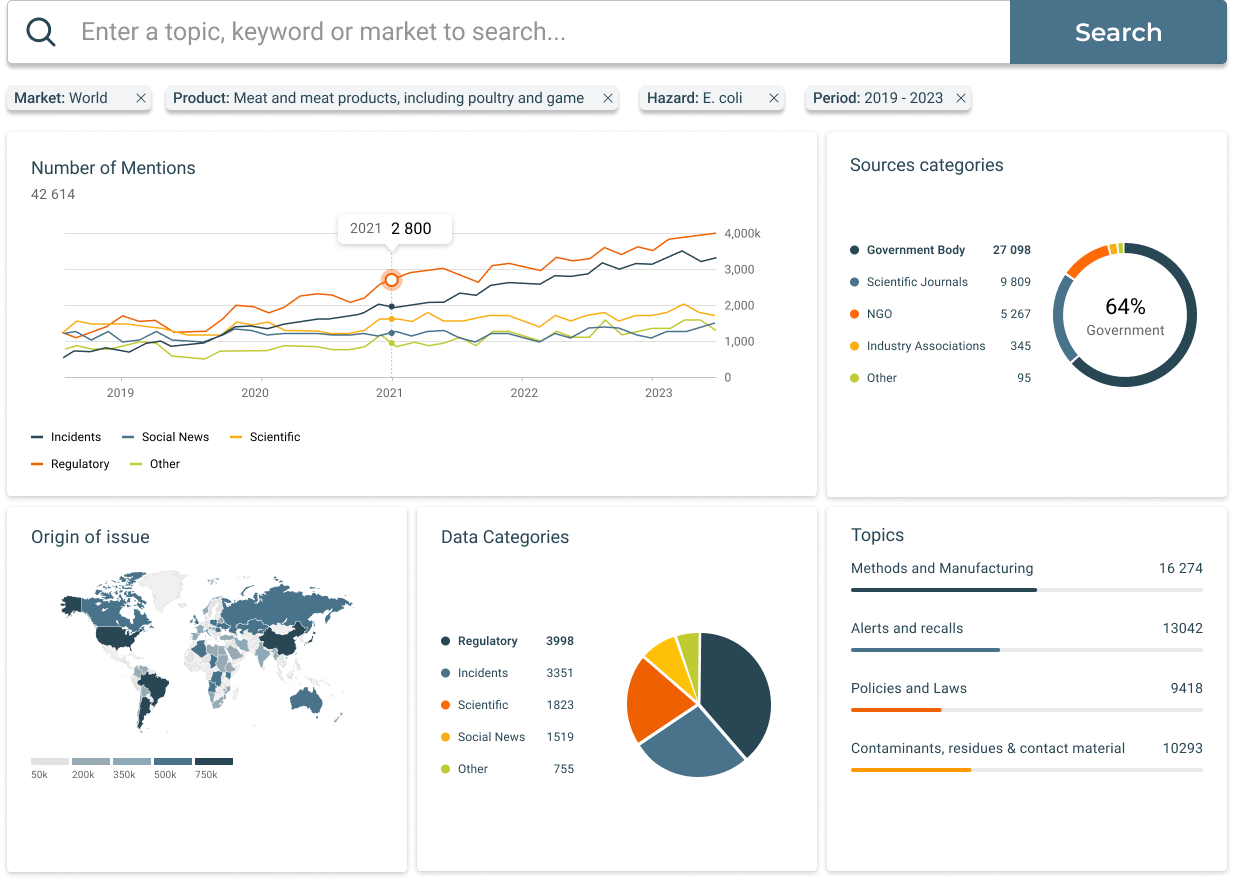
By combining diverse data sources, SGS Digicomply offers the most comprehensive and targeted screening of food safety data, contextualized with real-time lab data to identify emerging risks.





.webp?width=1644&height=1254&name=Food%20Safety%20Dashboard%201%20(1).webp)
