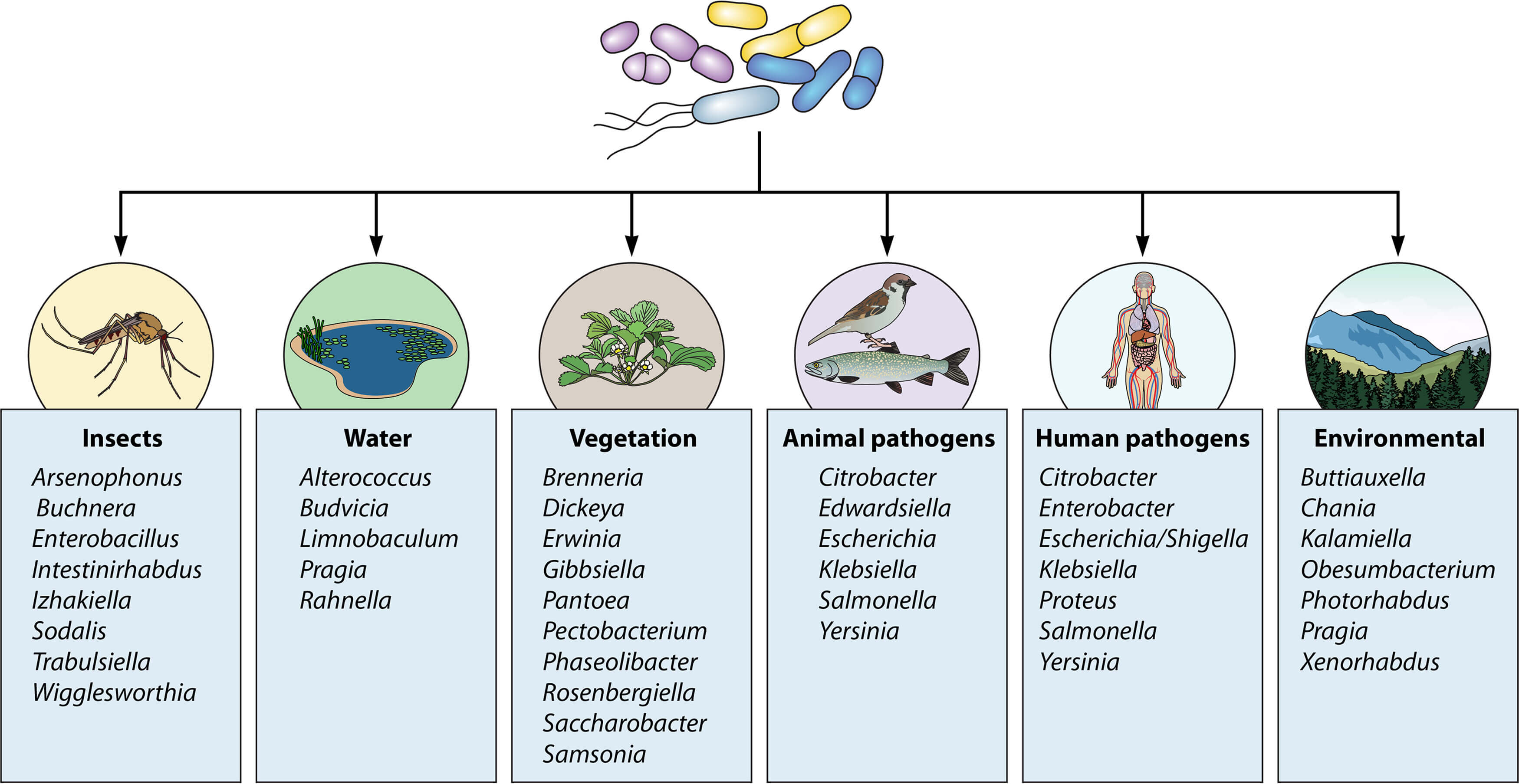
Enterobacteriaceae is a bacterial family encompassing a diverse group of organisms with both harmless and pathogenic members. Widely distributed in the environment, these bacteria play a crucial role in various ecological processes. However, the significance of Enterobacteriaceae extends beyond its environmental functions, as some strains pose a significant threat to public health, especially through the food chain.
Prevalence and Sources of Contamination
Enterobacteriaceae can be found in soil, water, and the gastrointestinal tracts of humans and animals. Its prevalence in the environment raises concerns about contamination of food products. Common sources include raw vegetables, undercooked meats, and unpasteurized dairy products. Poor food handling practices, inadequate sanitation, and cross-contamination during food processing contribute to the spread of Enterobacteriaceae in the food chain.
Potential Threats to Public Health
Consuming food contaminated with Enterobacteriaceae can lead to various foodborne illnesses. Strains such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), Salmonella, and Shigella are notorious for causing severe gastrointestinal infections. Symptoms range from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions, especially in vulnerable populations like the elderly and immunocompromised individuals. Real-world examples, such as the E. coli outbreak linked to contaminated lettuce in 2018, underscore the gravity of the issue.
Challenges in Prevention and Control
The food industry faces numerous challenges in preventing and controlling Enterobacteriaceae infections. Regulations play a crucial role, but enforcement varies globally. Monitoring food production processes, implementing stringent hygiene practices, and enhancing traceability are essential components of controlling contamination. Despite efforts, outbreaks continue to occur, highlighting the need for ongoing vigilance and improvement.
SGS Digicomply Insights: Rising Enterobacteriaceae incidents
In recent years, the trajectory of Enterobacteriaceae incidents has been a cause for concern, as highlighted by the data presented in SGS Digicomply Food Safety Intelligence Hub. From 2017 to 2019, there was a substantial increase, with incidents surging by approximately 222.22%. This alarming trend underscores the growing challenges in managing and mitigating the impact of Enterobacteriaceae-related issues. Looking at the broader timeline from 2017 to 2023, the situation becomes even more pronounced, with incidents soaring by a staggering 400.00%.
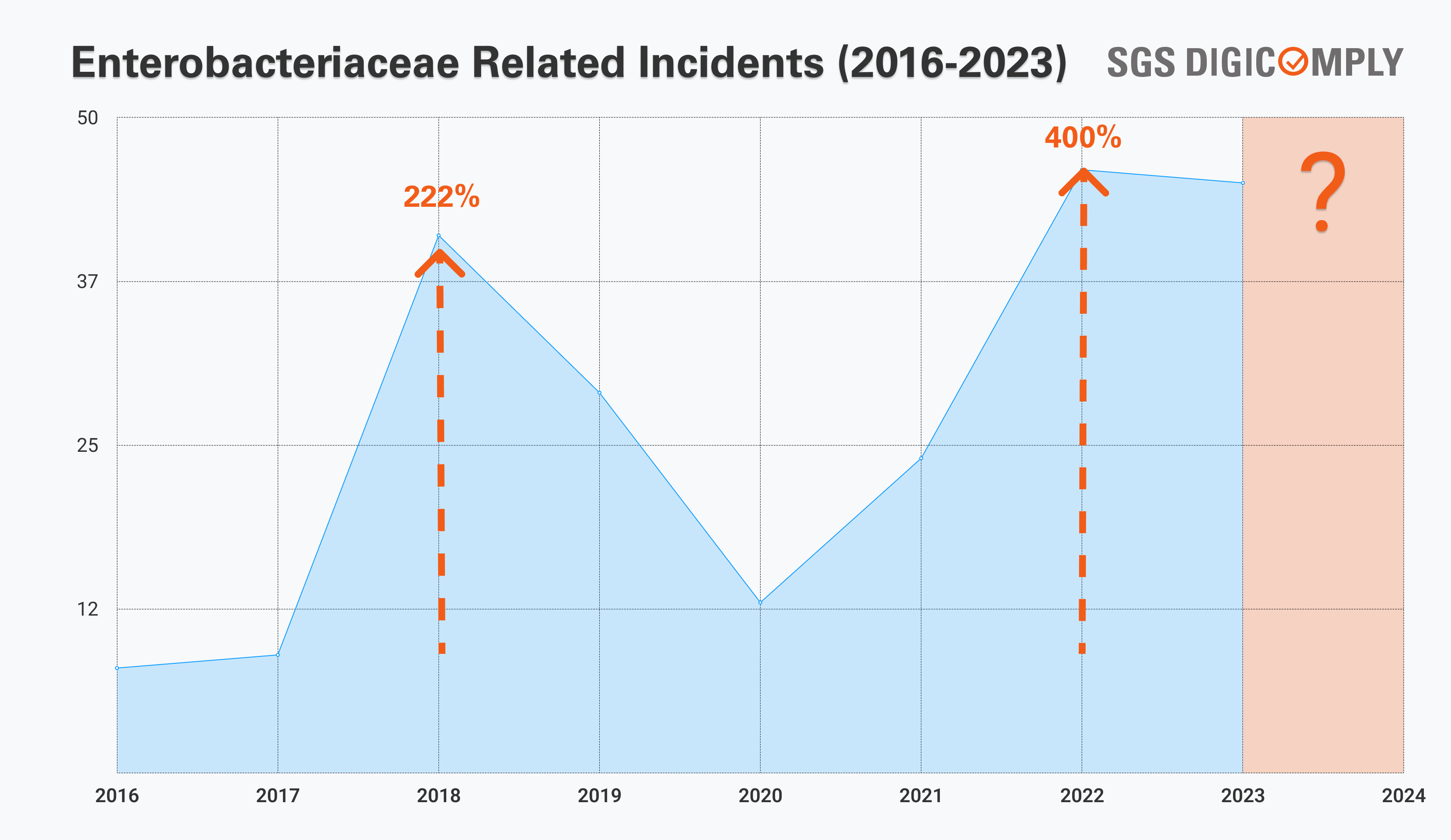
These numbers emphasize the urgency of addressing and understanding the factors contributing to the rise in Enterobacteriaceae incidents, calling for concerted efforts in enhancing food safety protocols, regulatory measures, and public awareness campaigns.
SGS Digicomply's Food Safety Intelligence Hub utilizes advanced AI technology, combining thousands of data sources to enable comprehensive yet targeted screening of food safety data and key insights. These insights are then contextualized with real-time laboratory data, allowing for the identification and connection of previously unseen emerging risks.
Feel free to get in touch now to learn about implementing the Food Safety Intelligence Hub for your company.
Antibiotic Resistance and Treatment Implications
Enterobacteriaceae's ability to develop antibiotic resistance poses additional concerns. Strains like extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) and carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) limit treatment options, leading to increased morbidity and mortality. The misuse of antibiotics in both humans and animals contributes to the development and spread of resistant strains, emphasizing the importance of responsible antibiotic use.
Ongoing Research and Innovations
Researchers are actively exploring new strategies to address Enterobacteriaceae-related public health concerns. Innovations include the development of rapid detection methods, advanced food processing technologies, and alternative antimicrobial agents. Collaborative efforts between the scientific community, food producers, and policymakers are crucial for staying ahead of emerging challenges.
Enterobacteriaceae poses a significant threat to public health through the food chain, necessitating comprehensive strategies for prevention and control. Stringent regulations, improved monitoring, and heightened hygiene practices are vital components. Addressing antibiotic resistance requires a global commitment to responsible antibiotic use. Ongoing research and innovation will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of food safety, emphasizing the need for collaboration across sectors to safeguard public health. Minimizing the risks associated with Enterobacteriaceae requires a collective effort from individuals, food producers, and policymakers alike.




.webp?width=1644&height=1254&name=Food%20Safety%20Dashboard%201%20(1).webp)
