Food safety monitoring is one of the major concerns of public health in that it ensures the food consumed is safe, wholesome, and free of any toxic contaminants. A proper monitoring mechanism averts the chances of foodborne diseases, provides assurance about regulatory compliance, and builds trust in consumers. Advanced technologies and tools are required to ensure efficient and accurate food safety monitoring in the context of ever-complexifying global food chains.
The article discusses some of the key elements contributing to food safety monitoring and emphasizes how SGS Digicomply plays a very important role in scaling these efforts through some innovative solutions and wide compliance support.
What is Food Safety Monitoring?
Food safety monitoring is a systematic approach toward the identification, assessment, and management of risks associated with food production and distribution. The program is focused on the safety of food through the continuity of incidents and trends tracking for compliance with regulations to prevent foodborne illnesses and to ensure consumer safety.
Definition and Scope
Food safety monitoring is the observation of conditions in real-time that can impact food safety, including contamination incidents, recall notifications, and breaches of compliance. It defines all activities aimed at maintaining food safety from farm to fork.
Key Components and Processes
- Incident Tracking: The process of monitoring and documenting a food safety incident, for example, contamination reports, recalls, outbreaks.
- Risk Assessment: Assessment of possible magnitude and likelihood of occurrence of an identified hazard.
- Compliance Monitoring: Ensuring that food production and handling processes adhere to the set standards of safety and regulations.
- Data Analysis: Conducting trend and pattern analysis of food safety incidents using data analytics tools to predict and help prevent future potential risks.
- Communication and Reporting: Stakeholder reporting on food safety incidents, regulatory changes, and compliance status.
The Benefits of Proactive Food Safety Monitoring
Proactive monitoring and control of food safety risk factors is based on the principles of continuous assessment and treatment of any potential risks before they become critical. It is an important implementation that aids in realizing a number of considerable advantages connected with food safety monitoring:
- FOODBORNE ILLNESSES PREVENTION. As a result of the realization of early risk identification and mitigation, proactive monitoring prevents the occurrence of foodborne illnesses and hence ensures consumer safety and public health.
- REGULATORY COMPLIANCE. Continuous monitoring provides adherence to the food manufacturing process in full compliance with changing regulations and standards, mitigating the risk of penalties for non-compliance.
- BRAND PROTECTION. High standards of food safety enhance an organization's reputation with consumers who have started to build trust in an organization and are loyal customers.
- COST SAVINGS. Pro-active steps may reduce the adverse costs of recalls, litigation, and loss of consumer confidence.
- DATA-DRIVEN DECISION MAKING. Pro-active monitoring is based on data analytics to drive actionable insights that will enable the business to make informed decisions and to continue improving their food safety practices.
How to Conduct Food Safety Monitoring: A Detailed Step-by-Step Plan
1. Establish a Monitoring Plan
- Define Objectives: Outline the goals and scope of your food safety monitoring efforts.
- Identify Key Areas: Focus on critical control points (CCPs) in the production and supply chain.
- Set Standards: Determine the food safety standards and regulations applicable to your operations.
2. Implement Advanced Technologies
- Real-Time Monitoring Systems: Use sensors and IoT devices to continuously track environmental conditions and detect contaminants.
- Predictive Analytics: Employ data analytics to predict potential risks and prevent incidents.
- Blockchain for Traceability: Utilize blockchain technology to ensure transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain.
3. Conduct Regular Audits and Inspections
- Routine Checks: Schedule regular audits and inspections to verify compliance with safety standards.
- Random Sampling: Perform random sampling of products to test for contaminants and ensure quality.
- Third-Party Audits: Consider using third-party auditors to provide an unbiased assessment of your food safety practices.
4. Employee Training and Awareness
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Develop and implement training programs for all employees involved in food production and handling.
- Ongoing Education: Keep employees informed about the latest food safety practices and regulations.
- Safety Culture: Foster a culture of food safety within the organization, emphasizing the importance of each employee's role in maintaining standards.
5. Leverage Data and Continuous Improvement
- Data Collection: Collect and analyze data from monitoring systems, audits, and inspections.
- Identify Trends: Use data to identify trends and patterns that could indicate potential risks.
- Implement Improvements: Based on data analysis, make necessary adjustments to your monitoring plan and processes.
- Feedback Loop: Establish a feedback loop where insights from data analysis inform ongoing improvements in food safety practices.
6. Communication and Reporting
- Incident Reporting: Develop a system for promptly reporting food safety incidents to relevant stakeholders.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure all monitoring activities and incidents are documented to meet regulatory requirements.
- Stakeholder Communication: Keep all stakeholders, including employees, suppliers, and customers, informed about food safety measures and any incidents.
Only the structured step-by-step plan will efficiently manage food safety monitoring in the light of all the emerging risks, ensuring that associated risk factors remain under control to protect public health and comply with food safety regulations.
AI-Powered Food Safety Monitoring with SGS Digicomply
Businesses leverage SGS Digicomply to empower artificial intelligence in food safety monitoring. From it, they enable cutting-edge tools to manage risk proactively and be compliance-ready.
Food Safety Intelligence Hub
Food Safety Intelligence Hub is at the core heart of proactive monitoring of food safety. The tool pulls together data from thousands of sources, including government alerts and recall notifications, so as to provide correct insights into potential food safety hazards. On top of this real-time data monitoring and analysis, the hub enables the timely notification of contamination incidents or growing risks. This proactive stance keeps companies ahead of threats and makes sure that proper risk mitigation measures are being taken before they grow. Check out these demos to see it in action.
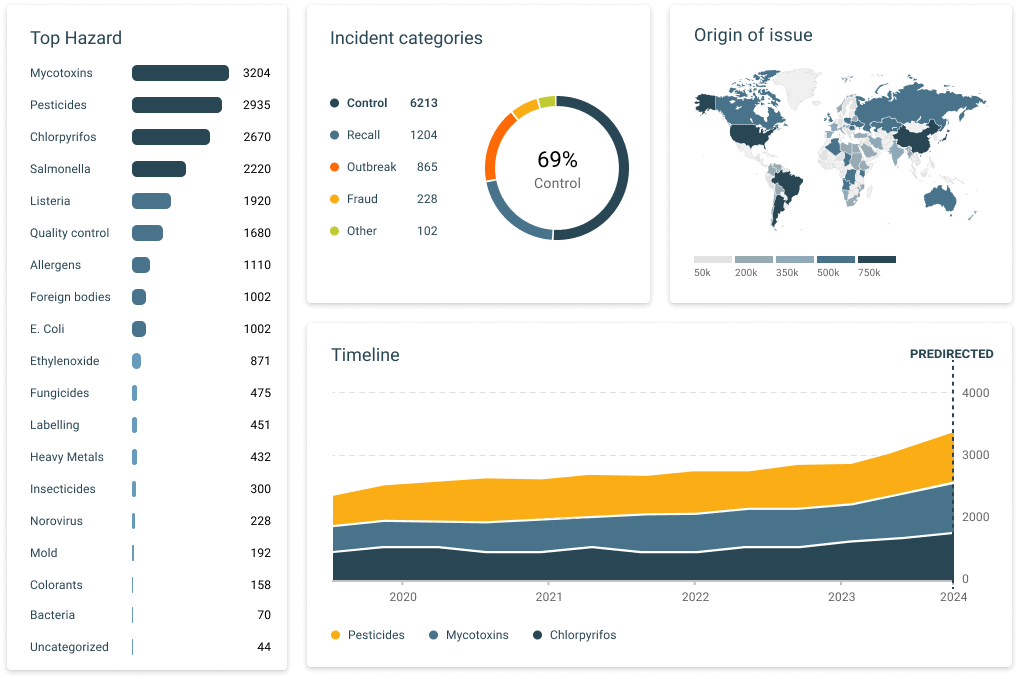
Regulatory Intelligence Hub
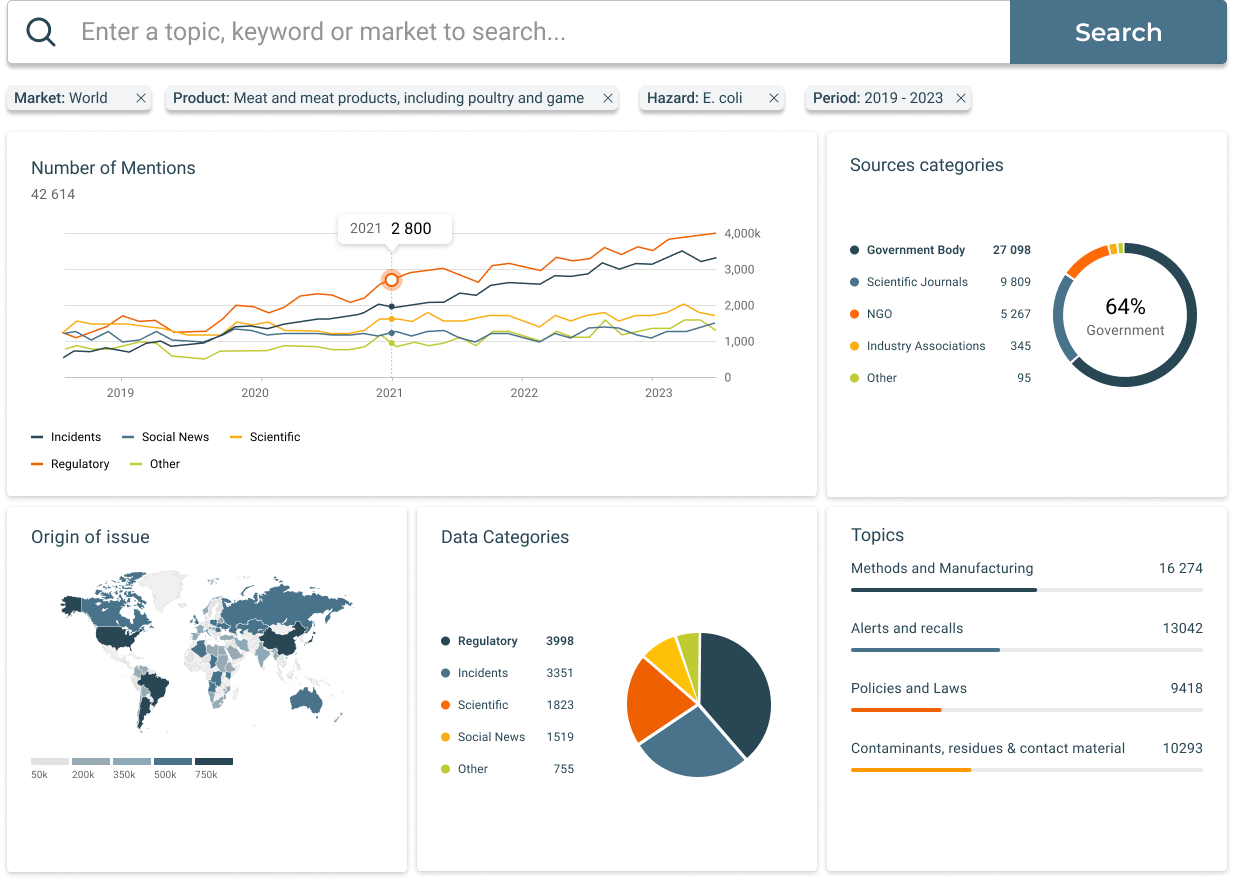
Ensuring compliance with ever-changing food safety regulations is critical. The Regulatory Intelligence Hub simplifies this process by providing access to a vast regulatory database covering over 150 jurisdictions. This feature uses AI to monitor and analyze regulatory changes in real time, offering up-to-date insights and alerts on new or amended regulations. This allows businesses to quickly adapt their practices to remain compliant, thereby avoiding potential fines and ensuring continuous adherence to global food safety standards. Check out these demos to see it in action.

Global Ingredient Monitor
Monitoring the safety and compliance of ingredients used in food production is crucial. The Global Ingredient Monitor offers a comprehensive solution by providing data on legal limits, usage restrictions, and banned substances worldwide. This tool allows businesses to navigate ingredient regulations by country and product, and set up alerts for any regulatory changes. By ensuring that all ingredients meet the necessary safety standards, companies can prevent the use of non-compliant substances and reduce the risk of food safety incidents. Check out these demos to see it in action.

Horizon Scanning
Horizon Scanning is a proactive tool designed to identify and anticipate future food safety risks. This feature monitors a broad range of data points, including supply chain dynamics, emerging biological, chemical, and physical hazards, and technological advancements. By analyzing these trends, businesses can predict and prepare for potential threats, ensuring that they are well-equipped to handle new challenges as they arise. Horizon Scanning helps maintain a forward-looking approach to food safety, enabling companies to stay ahead in an ever-evolving industry. Check out these demos to see it in action.
Integrate cutting-edge features, and enhance the efficiency of food safety monitoring with SGS Digicomply to ensure that companies not only adhere to existing regulations but also can proactively control and avoid risk factors. The holistic approach guarantees the highest level of quality food safety standards while simultaneously protecting public health and brand reputation.





.webp?width=1644&height=1254&name=Food%20Safety%20Dashboard%201%20(1).webp)
