In the ever-evolving landscape of food safety and regulatory measures, the debate over the use of titanium dioxide (TiO2) in food products has emerged as a significant point of contention among scientists, regulatory bodies, and consumers. Titanium dioxide, a white, powdery substance, is widely used for its ability to enhance the brightness and color of foods, cosmetics, and other products. However, its safety, particularly when ingested, has become a hot topic of discussion, leading to a reevaluation of its role in the food industry.
What is Titanium Dioxide?
Titanium dioxide is a naturally occurring mineral used in a variety of applications for its pigmentation and opacifying properties. In the food industry, TiO2 is used to give a whiter, brighter appearance to products such as candies, pastries, chewing gum, and even some dairy products. Its application is not limited to food; titanium dioxide is also prevalent in sunscreens, paints, and pills, serving as a pigment or a protective coating.
An Overview of Titanium Dioxide-Related Incidents: Navigating Safety from 2020 to 2023
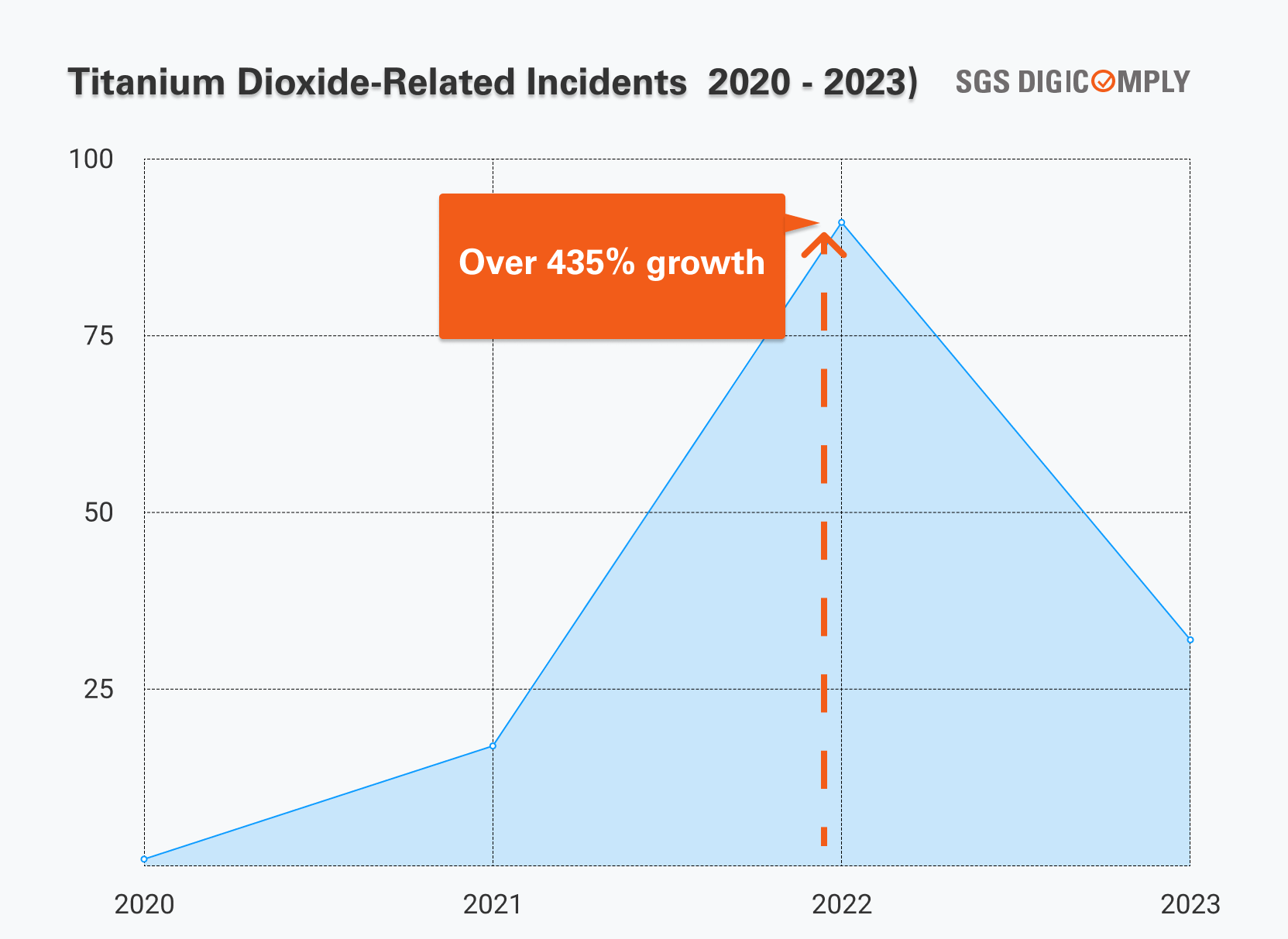
For our analysis, we utilized the SGS Digicomply platform, specifically the Food Safety Intelligence module. Upon examining the trend of incidents related to Titanium Dioxide over the last three years (2022-2023), we observed a sharp spike in incidents in 2022, with an increase of 435%. Although this surge diminished by 2023, the level of incidents remains high. It's also important to highlight that over 70% of all incidents were related to Contaminants. Moreover, incidents were most frequently reported in the United States of America and France, with several cases also noted in the United Kingdom, China, India, Taiwan, Spain, the Dominican Republic, Türkiye, and Canada.
Feel free to get in touch now to learn about implementing the Food Safety Intelligence Hub for your company.
Safety Concerns
The primary concern regarding the use of titanium dioxide revolves around its particle size. In some forms, TiO2 contains nanoparticles, which are tiny particles that can penetrate cell membranes. Studies have raised concerns that these nanoparticles could accumulate in the human body, potentially leading to toxicological effects. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has classified titanium dioxide as a Group 2B carcinogen, which means it is "possibly carcinogenic to humans" based on inhalation studies in rats, although direct evidence in humans, particularly through ingestion, is lacking.
Regulatory Stance
The regulatory stance on titanium dioxide varies significantly across the globe. In the European Union, for instance, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) announced in 2021 that titanium dioxide could no longer be considered safe as a food additive due to uncertainties about its impact on the human genome and potential to cause DNA damage. Consequently, a ban on the use of TiO2 in food products in EU countries is being implemented.
Conversely, in the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) continues to list titanium dioxide as a generally recognized as safe (GRAS) substance when used in accordance with good manufacturing practices. However, the FDA's stance has not gone without scrutiny, and there are calls for a reevaluation of its safety assessment in light of recent findings and the precautionary measures adopted in Europe.
Industry and Consumer Response
The debate over titanium dioxide has prompted a notable shift within the food industry, with some manufacturers voluntarily phasing out the use of TiO2 from their products. This move is partly in response to growing consumer demand for "clean label" foods, which are perceived as being natural and free from synthetic additives. The trend towards transparency and natural ingredients has accelerated the search for alternative whitening agents that can provide similar effects without the associated health concerns.
The Future of Titanium Dioxide in Food
The future of titanium dioxide in food is uncertain and likely to be shaped by ongoing research, regulatory decisions, and consumer preferences. As scientific understanding of its health impacts deepens, and as regulatory bodies around the world reevaluate their positions, we may see a shift towards stricter controls or outright bans on its use in food. In parallel, the food industry's innovation in developing safer and more natural alternatives will play a crucial role in determining whether titanium dioxide remains a staple of food production or becomes a relic of the past.
Conclusion
The debate over titanium dioxide in food underscores the complex interplay between scientific evidence, regulatory frameworks, and consumer expectations in determining the safety and acceptability of food additives. As we move forward, it will be essential for all stakeholders to engage in open, evidence-based discussions and to prioritize public health and safety in making decisions about the role of such substances in our food supply. The controversy over titanium dioxide is more than a question of aesthetics; it is a matter of public health, environmental responsibility, and consumer rights.





.webp?width=1644&height=1254&name=Food%20Safety%20Dashboard%201%20(1).webp)
